Overview
Heart attacks can be very dangerous and even life-threatening. The lack of blood flow to the heart can cause damage or death to part of the heart muscle. This damage can lead to long-term problems such as heart failure or an irregular heartbeat, which can further increase the risk of death.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 2.8 million deaths occur annually due to CVD in India. Ischemic heart disease and stroke account for 80% of all CVD deaths in India.
- According to the American Heart Association, about 790,000 Americans have a heart attack each year.
- In the United Kingdom, the number of people who die from a heart attack each year is around 92,000.
Read on to understand how narrowed or blocked blood vessels are treated, and any risks associated with the procedure.
Understanding Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked blood vessels in the heart. It involves using a catheter (a thin tube), which is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the area of the blockage. A balloon at the end of the catheter is then inflated to widen the blood vessel. While angioplasty can be an effective treatment for heart disease, there is a small risk of complications, including heart attack.
Statistics show that over 2 million people worldwide undergo coronary angioplasty each year.
What are the causes of a heart attack after angioplasty?
There are several potential reasons why someone might have a heart attack after angioplasty:
Causes | Description |
| Restenosis | A condition that occurs when the blood vessel becomes narrowed again after the angioplasty procedure. This can decrease blood flow to the heart, increasing the risk of a heart attack. |
| Complications from the procedure | The angioplasty procedure itself carries a small risk of complications, including damage to the blood vessel or a torn artery. |
| Other underlying health conditions | A person with other underlying health conditions, like diabetes or high blood pressure, may be at a higher risk of a heart attack after angioplasty. |
| Clot formation | In some cases, a blood clot may form at the angioplasty site, which can block the blood flow to the heart and cause a heart attack. |
Let us understand more about potential complications after an angioplasty.
What are the major complications after angioplasty?
- Restenosis: This condition occurs when the blood vessel narrows again due to cells from the inner walls of the artery form scar tissue within the stent. Restenosis can impact the blood flowing to the heart, and increase the risk of a heart attack.
- Bleeding: There is a small risk of excessive bleeding at the site of catheter insertion.
- Allergic reaction: Some people may be allergic to the contrast dye used during the procedure.
- Infection: There is a small risk of infection at the site where the catheter was inserted.
- Complications from the procedure: The angioplasty procedure can carry a small risk of complications, including a tear in the artery or a blood vessel.
Read on to learn more about what to expect after an angioplasty.
What are the chances of a heart attack after angioplasty?
The overall risk of having a heart attack after angioplasty is low. The risk of a heart attack after angioplasty depends on various factors, including the patient's age, overall health, and the severity of the blockages in the coronary arteries. The risk can also depend on the type of angioplasty performed, such as whether stents are used.
According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the risk of experiencing a heart attack within the first week after angioplasty is less than 1%. The risk may be slightly higher for people with other underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
According to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the risk of a significant adverse cardiac event (MACE), which includes a heart attack, death, and the need for repeat revascularization, was 3.7% in the 30 days after angioplasty.
Here is a table that summarizes the risk of MACE by age group in the 30 days after angioplasty:
Age Group | Risk of MACE |
| < 55 years | 2.3% |
| 55-64 years | 3.2% |
| 65-74 years | 4.5% |
| > 75 years | 6.4% |
Note: However, please remember that these statistics may not apply to every individual. It is always best to discuss the specific risks and benefits of the procedure with your cardiac surgeon, who can take into account your personal medical history and circumstances and decide if you need to undergo go a heart surgery only in extreme cases.
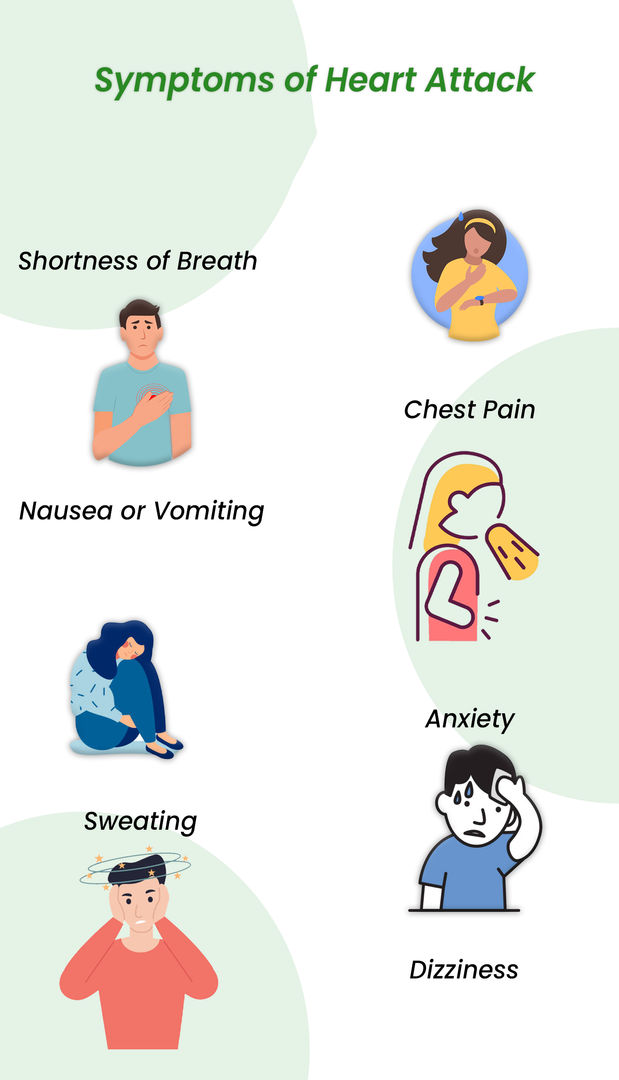
If you are experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, or sweating after angioplasty, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Let us learn about the prognosis after an angioplasty.
What is the life expectancy after angioplasty?
It is difficult to accurately predict someone's life expectancy after angioplasty as it will depend on a variety of factors, including:
- the overall health of the individual
- whether they have any other underlying health conditions
That being said, angioplasty can be an effective treatment for heart disease and can help improve heart function and quality of life. Many people who have undergone angioplasty are able to return to their normal activities and live long healthy lives.
Angioplasty is a lifesaving treatment for many, but it is important to know the risks, including the possibility of a heart attack.
Let us find out what can impact a good prognosis after an angioplasty.
Who is at risk for a heart attack after angioplasty?
Several factors can increase the risk of a heart attack after angioplasty. These include:
Risks | Description |
| Age | Older people may be at a higher risk of complications from angioplasty, including heart attack. |
| Other underlying health conditions | People with other underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, may be at a higher risk of experiencing a heart attack after angioplasty. |
| Severity of heart disease | People with more severe heart disease may be at a higher risk of experiencing a heart attack after angioplasty. |
| Complications during the procedure | As mentioned above, if there is any complication during the procedure, it can increase the chances of a heart attack. |
| Lifestyle | People who do not follow a healthy diet and lifestyle will have an increased risk of a heart attack. |
A heart attack can be a dangerous complication after angioplasty. But with the right knowledge and precautions, you can lower your risk and stay healthy.
How can you prevent a heart attack after angioplasty?
There are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of having a heart attack after angioplasty:
It is important to remember that while these steps can help reduce the risk of a heart attack after angioplasty, it is not always possible to prevent a heart attack completely.
Please ensure that you seek immediate medical intervention if you feel uneasy, have shortness of breath, or have chest pain after the angioplasty stent.
If you are considering an angioplasty or want to assess your health status after an angioplasty, do not delay any longer!
References:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-angioplasty/risks/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/coronary-angioplasty/about/pac-20384761