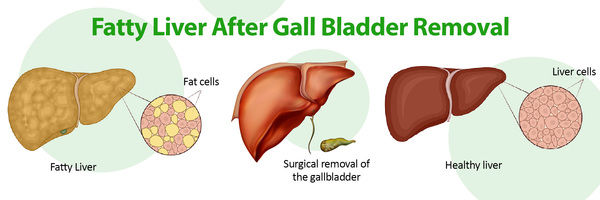
Cirrhosis is a serious liver condition that can lead to liver failure and other severe health complications, causing over half a million deaths globally every year. As a result, liver transplantation has become a crucial option for managing the disease's progression and improving patients' chances of recovery. Understanding the prevalence, treatment options, and survival rates for liver transplant patients across different regions is crucial.
According to the WHO, cirrhosis is the 12th leading cause of death globally. It is estimated that over half a million people die from the disease every year. Liver transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients with end-stage liver disease.
In the United States, cirrhosis is the 11th leading cause of death, with an estimated 30,000 people dying from the disease each year. The number of liver transplants performed in the US is also increasing. About 8,000 transplants are performed annually. The survival rate for liver transplant patients is high, with over 80% surviving at least one-year post-transplant.
In the UK, liver disease is the fifth most common cause of death, with cirrhosis significantly contributing to this statistic. In 2020, there were 1,711 liver transplants performed. The survival rate for liver transplant patients is also high.
In India, cirrhosis is a significant public health problem, with a prevalence of more than 10 million cases. The number of liver transplants performed in India is increasing. It is estimated that about 3,500 liver transplants are performed annually. However, the number of patients needing a transplant far exceeds the number of available organs, resulting in a significant waiting list for the procedure.
Please note that the statistics are estimated and the figures may vary in different regions of the country.
But why do people with liver cirrhosis need a liver transplant? Let’s find out.

Why do people with cirrhosis need a liver transplant?
Not all people with cirrhosis will require a liver transplant. The decision to undergo a liver transplant is based on the severity of the disease and the patient's overall health.
A liver transplant is typically considered for patients with end-stage liver disease. This condition is also known as decompensated cirrhosis or chronic liver failure. These are patients who have exhausted all other treatment options and have a poor prognosis without a transplant.
Are you now wondering if a liver transplant can fully cure cirrhosis?
Your well-being is our priority - call us to book your appointment today
Well, cirrhosis is a progressive disease caused by long-term damage to the liver, and it cannot be reversed. Scarring in the liver caused by the disease can't be undone. However, a transplant can replace the damaged liver with a healthy one, which can stop or even reverse the progression of the disease.
But patients must follow a strict regimen of immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their lives to prevent rejection of the new liver.
Note: A successful transplant can improve the patient's quality of life and extend their lifespan. But it does not cure the underlying cause of cirrhosis.
Continue reading to understand the factors that assess a possible candidate for a liver transplant.

Criteria for liver transplant in Cirrhosis
Patients with cirrhosis may be evaluated for transplant candidacy based on several factors, including:
- Presence of complications such as acute liver failure
- Variceal bleeding – bleeding in gastrointestinal tact
- Ascites – a collection of fluids in the abdomen
- Overall health
- Age
- The underlying cause of the cirrhosis
Patients who are considered candidates for a liver transplant will be placed on a waiting list for a suitable donor liver. However, the availability of donor's livers is limited. So not all patients who are candidates will be able to receive a transplant immediately.
Patients with cirrhosis need to work closely with their doctor to carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of a liver transplant. It is important to consider all treatment options before making a decision.
Take charge of your health and your life. Contact us today!

What are the common causes of cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver condition in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, leading to a loss of function.
The most common causes of cirrhosis are:
| Cause | Global Prevalence Rate |
| Alcohol is a leading cause of cirrhosis worldwide. | Estimated 20-50% |
| Hepatitis B, particularly in Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa | Estimated 25% |
| Hepatitis C, particularly in developed countries | Estimated 15% |
| Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), particularly in developed countries and regions with a high prevalence of obesity and diabetes | Estimated 24% |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | Estimated 2-5% |
Inherited metabolic diseases, like Wilson's disease, hemochromatosis, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and other genetic diseases, can also cause cirrhosis, and fatty liver.
It's worth noting that a combination of factors can cause cirrhosis, and it's not always possible to identify a single cause.
Preparing for a liver transplant for treating cirrhosis
Preparing for a liver transplant involves several steps, including:
Medical evaluation | You will need to undergo thorough a medical evaluation to determine if you are a candidate for a liver transplant, including:
You may also need to see a specialist in transplantation, such as a hepatologist or transplant surgeon, for further evaluation. |
Psychological evaluation | You will need to undergo a psychological evaluation to assess your emotional and psychological readiness for a transplant. This may include counseling or therapy to help you cope with the transplant process. |
Lifestyle changes | You will need to make lifestyle changes to improve your overall health and increase your chances of a successful transplant. This may include quitting smoking, losing weight, and avoiding alcohol.
|
Medications | You may need to take certain medications to manage your symptoms and prepare your body for transplantation. This may include medications to lower your bilirubin levels, control blood sugar and blood pressure, and prevent blood clots. |
Education | You will need to learn as much as possible about the transplant process and what to expect before, during, and after the transplant. This may include attending educational seminars and support groups and talking to other transplant patients and their families.
|
Financial Preparation | It would help if you considered the financial aspect. You will need to be prepared to pay for a transplant and the ongoing care and treatment costs. Insurance coverage, government programs, and other financial assistance may be available to help cover these costs.
|
Living Donor or Deceased Donor | You will also have to decide if you want to pursue a transplant from a living donor or wait for a deceased donor.
|
It's essential to remember that the transplant process can take some time and can be a stressful and emotional experience.
Now let's learn about the liver transplant procedure for cirrhosis.
The procedure of liver transplant for cirrhosis
A liver transplant is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased liver is replaced with a healthy liver from a donor. The procedure is typically done in stages, including:
Anesthesia | The patient will be given general anesthesia to put them to sleep during the procedure. |
The transplant surgery | The surgical team will make an incision in the patient's abdomen and remove the damaged or diseased liver. The new liver will then be placed in the patient's body and connected to the blood vessels, bile ducts, and other structures. |
Recovery | After the transplant surgery, the patient will be closely monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU) for several days to ensure that they are recovering properly. They will then be moved to a regular hospital room for further recovery and monitoring. |
Immunosuppressive therapy | The patient will be started on immunosuppressive therapy after the transplant to prevent their body from rejecting the new liver. This will typically involve a combination of medications that suppress the immune system. |
Follow-up care | After the transplant, the patient will need to see their transplant team regularly for follow-up care and monitoring. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and other tests to check the function of the new liver. |
Note: The recovery time and length of stay in the hospital can vary depending on the individual patient and their overall health.
So, now that the surgery is done, how long before you get back to your normal activities? Read on to find out.
How long does it take to fully recover from a liver transplant?
The recovery time after a liver transplant can vary depending on the patient's overall health. However, patients can expect to spend several weeks in the hospital and several months recovering at home.
Most patients can expect to return to normal activities within a few months, but it may take up to a year or more for a complete recovery.
As mentioned earlier, the patient will need to see their transplant team regularly for follow-up care and monitoring to check how well the new liver is functioning. They will be advised to take immunosuppressive medication to prevent their body from rejecting the new liver.
Furthermore, they must avoid alcohol and certain medications and follow a healthy diet. Physical therapy may be recommended to regain strength and endurance.
Take the first step to recovery. Get in touch with us for your treatment.
Note: The recovery time can vary based on factors such as age, overall health, and response to immunosuppressive therapy.
As in any surgery, there are a few side effects of the procedure that you need to be aware of.
The following are some of the most common side effects of a cirrhosis liver transplant:
- Pain or discomfort at the transplant site
- Infection
- Rejection of the transplanted liver
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Leakage of bile from the bile ducts
- Return of liver disease or development of new liver problems
- Adverse reactions to medications used to prevent rejection of the transplant
- Changes in mental function and emotional state
Note: Every patient is unique and may experience different side effects, some of which can be serious. Please monitor your health closely and talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
Now let’s take a look at the success rate of cirrhosis liver transplant!

How successful is a liver transplant for cirrhosis?
The success rate of liver transplantation for cirrhosis patients depends on various factors. These include the patient's overall health, the stage and severity of their liver disease, and the availability of a suitable liver transplant.
On average:
- the one-year survival rate after liver transplantation is around 80-85%.
- the five-year survival rate is around 70-75%.
However, it's important to keep in mind that these are rough estimates, and individual outcomes can vary.
Please remember that the success of a liver transplant is not just measured by survival rates. It is important to consider the improvement in quality of life and the ability to return to normal activities.
In general, liver transplantation can greatly improve a patient's health and prognosis, especially for those with advanced cirrhosis.
We hope we have helped provide you with a better understanding of cirrhosis and liver transplantation. If you have further questions, please know that we are here to guide you.
You can also learn more about cirrhosis and liver transplant by watching this video by one of the most reputed hepatologists.
References:
https://transplantsurgery.ucsf.edu/conditions--procedures/cirrhosis.aspx
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6876525/
https://www.hepatitisc.uw.edu/
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/liver-transplant
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/liver-transplant
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26585107/
https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cld.1061