The 18th and 19th centuries, which are most known for the industrial revolution and the conquering of empires, were also known as the 'age of pandemics'. Between 1817 and 1920, cholera, plague, and influenza pandemics occurred, each of which killed 70 million lives.
The cycle of plagues had the potential to become a global phenomena thanks to imperialism and international trade.
The irony of our progress in preventing infection-related deaths over the past 200 years is that it has contributed to foster the ideal environment for the emergence of new outbreaks, which will have devastating worldwide social and economic effects. Does that mean we are entering a new age of pandemics? As the COVID-19 pandemic slogs on, another viral disease has captured the world's eye; 'Monkeypox'
Global picture of monkeypox at present
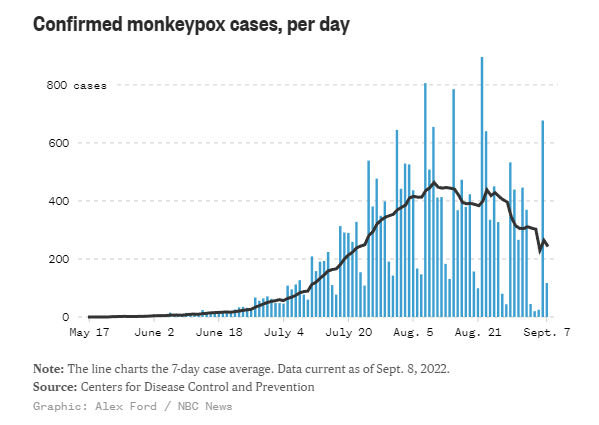
Since the start of May, the U.S. has officially documented more than 21,000 cases. While India reporting 10 cases in August and More than 56,000 people are involved globally. as per reports from August.
The monkeypox virus, is a zoonotic virus that typically only spreads from animals to humans but is related to the virus that causes smallpox, was first identified in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970. Africa has had sporadic outbreaks of illness, usually brought on by contact with wildlife reservoirs (particularly rodents). Due to the limited secondary spread of such epidemics and instances related with travel outside of Africa, it has been shown that human-to-human transmission is ineffective.
The World Health Organization declared monkeypox a "evolving danger of moderate public health concern" on June 23, 2022, after more than 3000 monkeypox virus infections were detected in more than 50 nations across five regions since early May 2022. Currently, countries in the European and North American regions are reporting the highest numbers of cases.
It's been there longer than we knew
The monkeypox virus has been circulating for decades in areas where it has been historically endemic, but research on the disease has been neglected and underfunded. Since 1958, when it was discovered in monkeys, the virus that causes monkeypox is not new. It was originally recognized as a human pathogen in 1970 after being first found in 1958 in study at a lab with monkeys. In west and central Africa, the illness has a long history of low endemicity. According to UNLV infectious disease expert Brian Labus, an epidemiologist and professor "There was a small outbreak in the U.S. Midwest in 2003, when pet prairie dogs – infected after being housed near rodents imported from Ghana – came in contact with humans."
All you need to know about Monkeypox
How is monkeypox transmitted?
The virus can spread among humans, primarily through close physical contact with an infected person or contaminated objects like clothes or bedding, or by the respiratory droplets produced when someone coughs, talks, or sneezes. Historically, people typically contracted monkeypox after coming into contact with infected animals.
What is driving the outbreak?
Data strongly suggests that sexual contact is the main mode of transmission because the vast majority of persons impacted by the global pandemic are (MSM). However, Professor Brian Labus adds that "There is a false belief, in my opinion, that monkeypox primarily affects males who have sex with other men (MSM) and that having MSM automatically guarantees you will contract monkeypox. Although it is true that the illness has spread among MSMs, we have also seen cases in children, family members, and non-MSMs."
How can monkeypox be treated?
The disease is usually self-limiting, meaning symptoms usually go away without the need for treatment within 2–3 weeks. Some people may require antibiotics and analgesia to treat secondary infections and local pain. While a new vaccine has been approved for the prevention of monkeypox, and the smallpox vaccine has also been demonstrated to provide protection. Dr. Faith Alex practicing medical doctor at Nationaltasc adds "Sometimes treatments for monkeypox help relieve symptoms but the virus will go away on its own. And, you can help yourself feel better by resting and drinking plenty of fluids."
What are the symptoms?
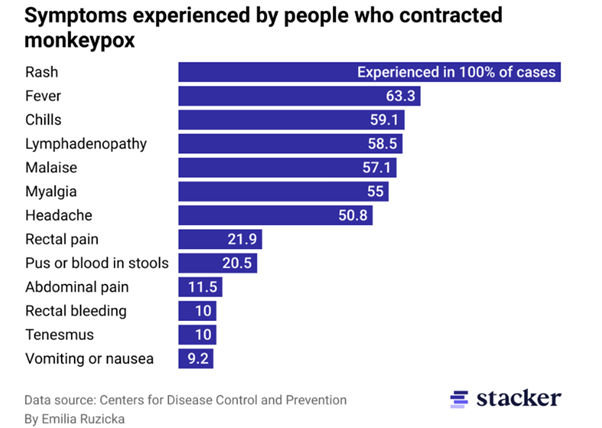
Monkeypox can cause flu-like symptoms like fever, headache, fatigue, chills, and enlarged lymph nodes and most people will develop a distinctive rash, though the extent of this can vary and clinicians have reported symptoms that are milder or more localized to genital and anorectal areas than previously expected
Someone who has contracted monkeypox usually starts to show symptoms between around 6–13 days after contact with an infected, symptomatic person, or their belongings, but it can take up to 21 days.
To conclude
With little resources for surveillance, diagnostics, and even patient care, the African nations where monkeypox is prevalent are still in the same condition as they have always been. Placide Mbala, a virologist at the Congo Institute of Biomedical Research, claimed that despite all the attention the West has given to monkeypox, nothing has changed in Africa. The UN health agency pleaded with the globe to aid African nations in preventing the tragic vaccination inequality that afflicted the COVID-19 outbreak.
Although new or previously confined infectious illnesses have been on the rise for decades, it seems as though we are currently witnessing a special uptick, from COVID-19 and monkeypox to Marburg and the new langya virus. We need to make our surveillance systems more robust in many parts of the world such that we are better able to identify outbreaks of novel pathogens.