The pancreas is an important organ in the body that is present in the abdomen. It produces digestive juices and hormones that help in the digestion of food and maintain proper functioning of the body respectively. This key organ produces insulin and glucagon which are required for maintaining the required blood sugar level in the body. It also allows the body to use and store the energy generated from food.
Pancreas transplant is one of the most preferred methods for treating diabetic patients in today’s time. Thus, understanding this technique is very important in order to educate oneself about its pros and cons.
In this article, you will get more information about pancreas transplants including:
· Different types of transplantation
· Procedures involved
· Potential risks associated with the transplantation.
In a pancreas transplant, a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor is placed in the body of a patient whose pancreas was diagnosed to not function properly. Pancreas transplantation is opted as a last resort but is considered a key treatment for diabetic patients.
A pancreas transplant aims to restore the normal functioning of the pancreas in the affected and is sometimes also suggested for cancer patients.
However, it is required to acknowledge here that a pancreas transplant is not the first preferred treatment by medical professionals as there are several risks associated with the procedure.
In a glance:
| Types |
|
|---|---|
| Risks associated | Post-surgery complications and side effects from anti-rejection medications |
| Waiting period to receive a donor | On average 1-2 years |
| Cost | Approximately, INR 15 Lakhs (19,663 USD) |
When is a pancreas transplant prescribed?
A pancreas transplant helps in restoring normal insulin production and improves blood sugar control.
It is considered as a treatment for patients in the following scenarios;
● For type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients
● Patient with blood sugar problems
● Kidney damage
● Frequent insulin reactions
Only 10% of pancreas transplants can be performed in cases for people suffering from type 2 diabetes because the body becomes resistant to insulin, which leads to other severe complications.
Understanding the types of Pancreas Transplant
Mentioned down below are some of the pancreas transplant techniques that can be conducted by a surgeon.
1. Only pancreas transplant: Solitary pancreas transplant is prescribed to patients who suffer from diabetes and do not have any other kidney ailments. In this case, a healthy pancreas of the donor is replaced with the pancreas of the recipient that is no longer functioning properly.
2. Combined kidney-pancreas transplant: In this case, a combined kidney-pancreas transplant is performed as the affected can be suffering from severe kidney damage or is at risk of kidney failure.
Pancreas transplant is performed at the same time as kidney surgery. The purpose of this procedure is to provide a healthy kidney that will not have the risk of suffering diabetes-related kidney damage in the long run.
3. Pancreas after kidney transplant: In this scenario, pancreas transplantation surgery takes place after the kidney transplant. However, the wait for a donor's pancreas or kidney can be time-consuming.
The pancreas transplantation takes place once the patient has recovered from a kidney transplant and a suitable donor pancreas is available.
4. Pancreatic islet cell transplant: For patients suffering from Type 1 diabetes, insulin-producing cells i.e., islet cells are taken from the donor pancreas and injected into the vein that carries blood to the liver of the donor.
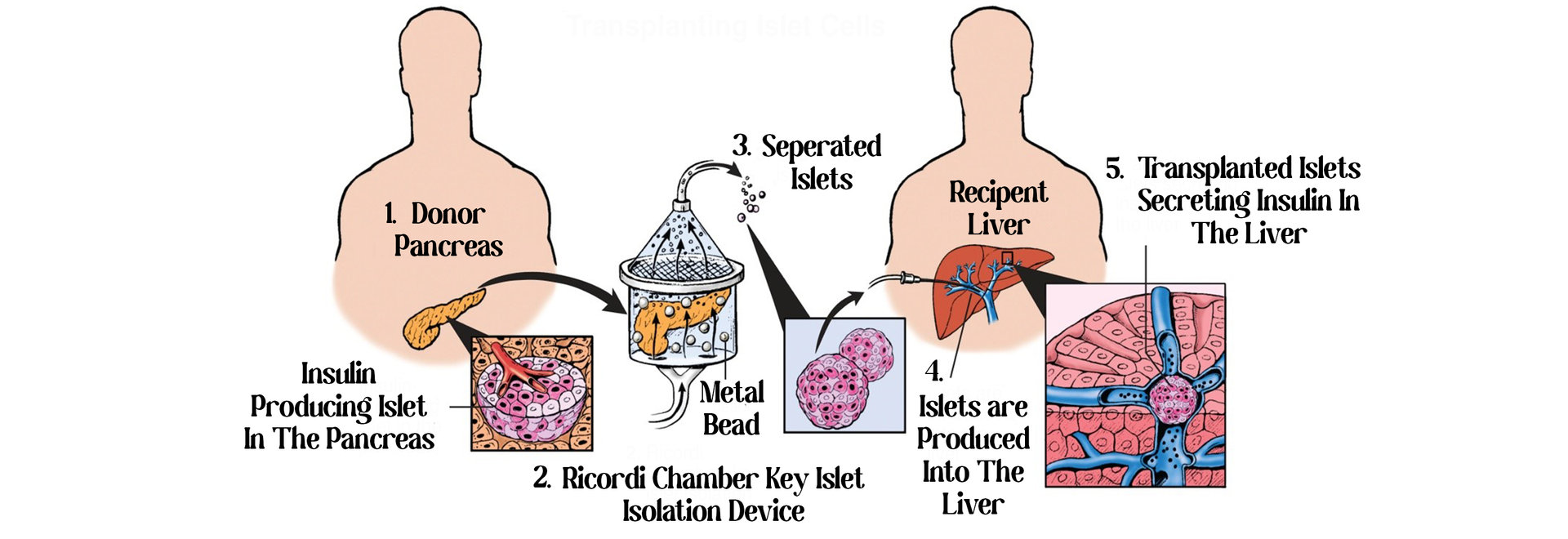
This transplant also helps in treating progressive complications that can occur due to Type 1 diabetes.
Now when we already know about the types of transplants, let's read how the transplants are done.
Understanding the Pancreas Transplant procedure
1. Post proper diagnosis when your medical advisor recommends a pancreas transplant, you can either be referred to a transplant center, or you can choose a center from the list of transplant centers provided to you by your insurance provider.
While choosing a transplant center, make sure you consider the following;
2. Evaluation tests need to be conducted on you to find whether you are eligible for the transplant or not. If yes, your name will then appear on the "National List" of people waiting for a transplant.
3. The donated pancreas should be from someone who has been pronounced brain dead but remains on life support. It is important to note that the donor's pancreas is properly functioning and healthy. The donor pancreas must also be a suitable match with the recipient's body immunologically.
4. Sometimes the donor of the pancreas can be living as well. In this case, the donor is a close relative or an identical twin of the recipient and gives a part of their pancreas to the recipient.
5. On average, it can take around one to two years for a recipient to receive a matching donor. If a patient needs to undergo combined surgeries, the waiting time can increase respectively.
While waiting for a suitable donor, it is important for the patient to,
● stay healthy
● follow diet and lifestyle habits that have been prescribed to you by your medical advisor
● avoid smoking
● consume prescribed medications
● stay active and involve in activities like exercising and relaxing.
What can you expect throughout the procedure?
1. While performing a pancreas transplant, surgeons administer general anesthesia to the patients to make them unconscious.
2. Then an incision is made in the center of the patient's abdomen. The new pancreas along with a small portion of the donor's small intestine is placed into the lower abdomen. Blood vessels are connected. The recipient's pancreas is left in the usual place to aid digestive functions.
3. If the patient's pancreas transplant is followed by kidney surgery, the new kidney gets attached to the lower abdomen with blood vessels being attached to it. The ureter of the new kidney gets attached to the bladder of the recipient and if the recipient's kidneys are not producing any complications, they are left in the usual place.
4. Pancreas transplantation surgery lasts for three to six hours depending on whether the patient is having solitary kidney transplantation or combined surgeries. During the surgery, the surgical team monitors blood oxygen, heart rate, and blood pressure throughout the surgery for possible development of complications.
What should you expect post surgery?
1. Once the pancreas transplantation has taken place, you will have to stay in the intensive care units for a couple of days. Medical professionals monitor your condition and seek possible signs of complications. The new pancreas is supposed to start working immediately while the older pancreas continues to aid normal functions in the body.
2. If you have a combined kidney and pancreas transplant, your new kidney is supposed to start making urine. However, in certain cases, normal urine production can take a couple of weeks.
3. Once the surgical team decides that the condition has been stabilized, the surgical team moves you from the intensive care unit and you are discharged soon after. However, close monitoring needs to be continued after you leave the hospital and a checkup schedule gets designed customarily for you.
4. The medical professionals provide medications that need to be taken for the rest of the your life. Medications like immunosuppressants and additional drugs are provided so that the immune system of the recipient does not attack the new pancreas and to also reduce the risk of infections and other complications respectively.
What are the potential risks of pancreas transplants?
A pancreas transplant is always considered as a last resort for patients because there are several risks that are associated with the transplantation and in some extreme cases can also lead to fatality.
Some of the significant complications associated with pancreas transplant are;
● Excessive bleeding
● Blood clots
● Infections
● Urinary tract infections causing urinary complications
● Hyperglycemia i.e., excess sugar in the blood
● Rejection of the donated pancreas by the recipient body
● Failure of the surgery
Anti-rejection medications are prescribed to the patient to help the body prevent rejecting the donated pancreas. These medications are supposed to be taken throughout the patient's life and these medications can cause several side effects. These medications tend to suppress the immune system of the recipient, making it difficult to immunize itself from potential diseases and infections.
Side effects include;
● Increased cholesterol levels
● Increased blood pressure
● Osteoporosis
● Sensitivity to light, especially sunlight
● Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting
● Swollen gums and puffiness
● Weight gain
● Excessive or loss of hair
● Acne
What are the success rate of pancreas transplant?
The success rate of a pancreas transplant depends upon:
- The condition of the patient
- The transplant center
- Surgeon, etc.
The pancreas will start producing insulin immediately if the body has completely accepted the new pancreas. However, with the best medications provided to treat, the recipient's body can reject the new pancreas. Anti-rejection medications are therefore prescribed to the affected to suppress rejection but that can make the recipient vulnerable to infections.
It is recommended to seek immediate medical attention if you observe symptoms like:
1. severe pain
2. excessive tenderness
3. decreased urination
4. fever
The above mentioned symptoms can indicate the body is rejecting the new pancreas.
It is normal to feel overwhelmed with pancreas transplant surgery. There are several assistance groups you can seek assistance from. Also, feel free to ask questions to your medical advisors. After the surgery, following a healthy lifestyle is an absolute must as it helps in keeping post-surgery complications at bay.