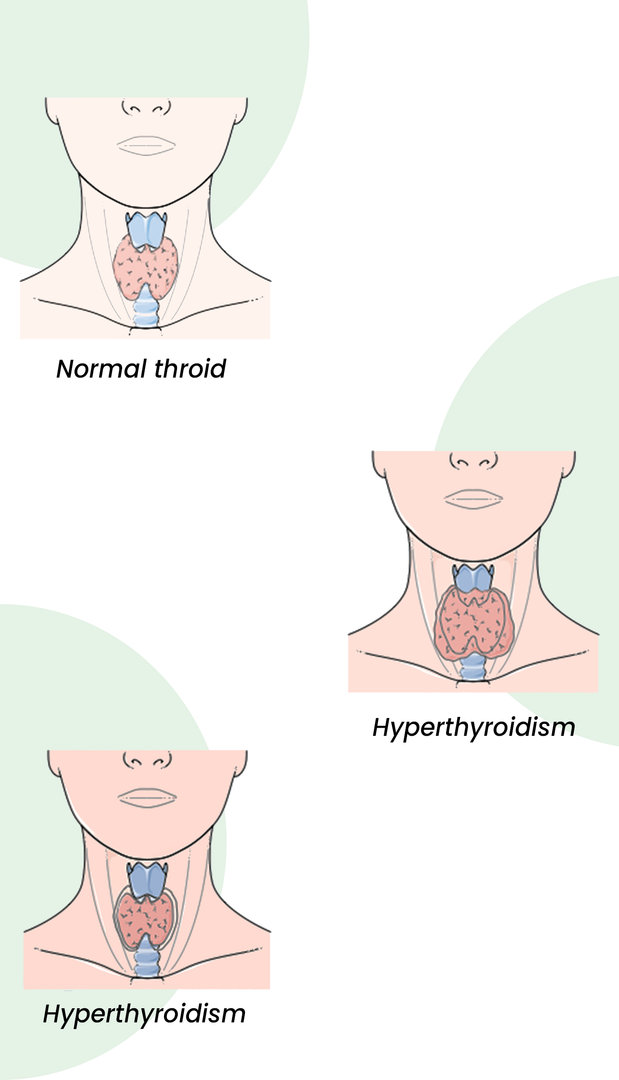
Can Thyroid Cause Itchy Skin?
yes, thyroid disorders can lead to various skin problems, including itchiness. Hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, can cause the skin to become dry and itchy. This is due to the slowed metabolism, which reduces sweating and leads to dry, flaky, and itchy skin. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces excessive hormones, can also cause itchy skin due to increased blood flow.
Did you know?
Statistics show that 20% with hypothyroidism and 5% with hyperthyroidism experience itchy skin.
By better understanding the connection between the thyroid and itchy skin, you can better understand how to identify and address the underlying cause.
Experiencing itchy skin? Schedule your consultation with top dermatologists now for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.

Itchy skin can be more than just a minor annoyance. How can a thyroid disorder cause itchy skin? We'll dive into how thyroid issues might be the underlying cause.
Many factors can cause itchy skin; thyroid dysfunction is just one of them.
Hypothyroidism:
- It occurs when the thyroid underproduces hormones.
- Low hormone levels can lead to dry, itchy skin.
- More noticeable in dry winter months.
Hyperthyroidism:
- Results from excessive thyroid hormone production.
- Causes itchy, sensitive skin.
- Accompanied by symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, stress, and anxiety.
Dr. Anju Methil, a Dermatologist in Mumbai, says, "Thyroid hormones play a vital role in regulating skin function, and imbalances can lead to various skin issues, including dryness, rash, and itching. Hypothyroidism, characterized by low thyroid hormone levels, is often associated with dry, coarse skin that is prone to itching. On the other hand, in hyperthyroidism, excessive thyroid hormone production happens, which can cause skin flushing and increased sensitivity, leading to itching and irritation. Proper management of thyroid disorders through medication and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for relieving skin symptoms and promoting overall skin health."
A study in The Journal of General Internal Medicine shows that 74% of hypothyroid patients report dry skin, and many say their skin issues worsen over time. Changes in the skin that cannot be attributed to allergies or new products could be indicative of a thyroid problem. In rare cases, Hashimoto's can sometimes develop an extreme form of itchy, dry skin, which can develop into urticaria or chronic hives. In a 1980s study, approx 12% of those with chronic urticaria also showed evidence of having Hashimoto's.
Let's get into the details: From diagnosis to treatment, discover how to manage itchy skin caused by thyroid problems and improve your overall well-being.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Disorders for Itchy Skin
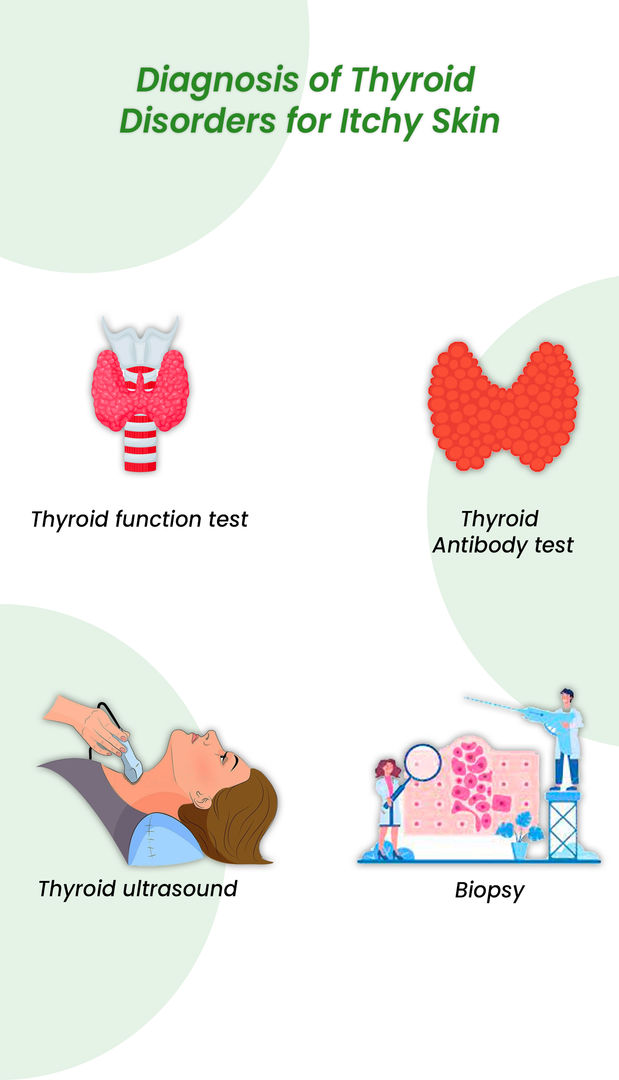
When it comes to diagnosing thyroid disorders that may be causing itchy skin, several tests may be used to get a clear picture of what's happening in the body.
Thyroid Function Tests:
- Measure T3, T4, and TSH levels in the blood.
- Abnormal hormone levels may indicate a thyroid disorder contributing to itchy skin.
Thyroid Antibody Tests:
- Determine if the thyroid disorder is autoimmune.
- Elevated thyroid antibody levels signal an immune system attack on the thyroid.
Thyroid Ultrasound:
- Evaluate thyroid gland size and shape and detect abnormalities.
- Identifies nodules that may cause thyroid dysfunction.
Biopsy:
- Further evaluation of nodules or abnormalities detected in a thyroid ultrasound is performed.
- Determines if nodules are cancerous or benign.
Skin Biopsy:
- If itchy skin is the primary concern.
- Rules out other causes like eczema, psoriasis, or fungal infections.
A combination of these tests may be used to diagnose thyroid disorders that contribute to itchy skin.
Overall, itchy skin can be a frustrating symptom of thyroid disorders, but it can often be managed with proper treatment and self-care measures.
Learn how to manage thyroid-related itchy skin get in touch and book an appointment with the skin specialists today! for expert tips and advice.
Thyroid Itchy Skin Treatment

- Prescription antihistamines: Your doctor may prescribe stronger antihistamines to relieve itching caused by allergies or skin conditions.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching. They are available in topical creams, oral tablets, and injectable forms.
- Topical creams or ointments: Your skin expert may prescribe topical creams or ointments containing ingredients like hydrocortisone, coal tar, or calcineurin inhibitors to relieve itching and reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive drugs: Immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed for severe itching caused by autoimmune skin conditions.
- Light therapy: Light therapy, or phototherapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Biologics: Biologics are medications that target specific proteins in the body to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. They may be prescribed for severe itching caused by autoimmune skin conditions.
Looking for relief from itchy skin? Here are some tips to help you prevent itchy skin due to your thyroid!
How to Prevent Itchy Skin in the Thyroid?
- Avoid hot showers or baths: Hot water can strip your skin of natural oils and exacerbate dryness, leading to itchiness. Take short, lukewarm showers or baths instead.
- Moisturize regularly: Apply fragrance-free cream after showering to hydrate and prevent dryness.
• Gentle soap: Use mild, fragrance-free soap to avoid irritation.
• Breathable clothes: Wear loose, soft clothing from natural fibers like cotton.
- Avoid scratching: Although tempting, scratching can further irritate your skin and cause damage. Try using a cool compress or applying a topical cream to relieve itching.
- Manage stress: Stress can worsen skin conditions and cause itching. To manage stress levels, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
Please Note: These tips may help relieve itchy skin but do not address the underlying thyroid condition causing the symptom. Therefore, it's essential to continue following your thyroid treatment plan as your thyroid doctor prescribes.
What Happens if Thyroid Dysfunction and Itchy Skin are Left Untreated?
Worsening Symptoms: Fatigue, weight changes, and skin issues can become more severe.
Heart Problems: Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to heart palpitations, high blood pressure, and heart failure. Hypothyroidism can cause a slow heart rate and increased cholesterol levels.
Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, depression, and mood swings can worsen without treatment.
Reproductive Issues: Untreated thyroid disorders can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and complications during pregnancy.
Neuropathy: Long-term untreated hypothyroidism can cause nerve damage, leading to tingling and numbness in the extremities.
Myxedema: Severe, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to myxedema, a life-threatening condition that causes extreme fatigue, cold intolerance, and swelling.
Goiter Development: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid gland that can lead to difficulty swallowing or breathing.
References:
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/thyroid-disease-skin-changes