Blood Cancer
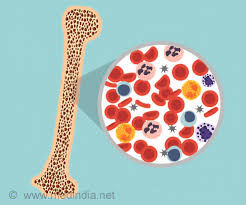
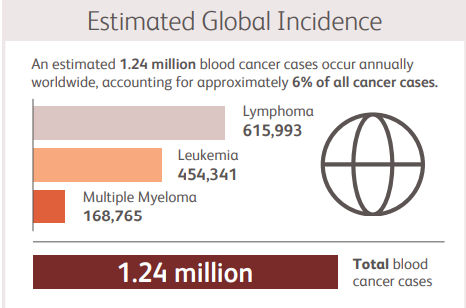
An estimated 1.24 million new cases of blood cancer are reported each year, making up around 6% of total cancer cases. Hematologic cancers, also known as blood cancers, interfere with the development and operation of blood cells. Cancers like these frequently begin in the bone marrow where blood is made. More than 7% of all cancer-related deaths are caused by blood cancer, which claims about 720000 lives annually worldwide. There are many ways you can prevent blood cancer and many treatments are available to cure but it majorly depends on the type of cancer and severity of it. There are many types of blood cancer such as Leukemia, Lymphoma, Multiple myeloma, and many more.
Blood cancer can be a difficult topic to discuss, but breaking the silence is important
So let’s discuss it!
What Causes Blood Cancer?
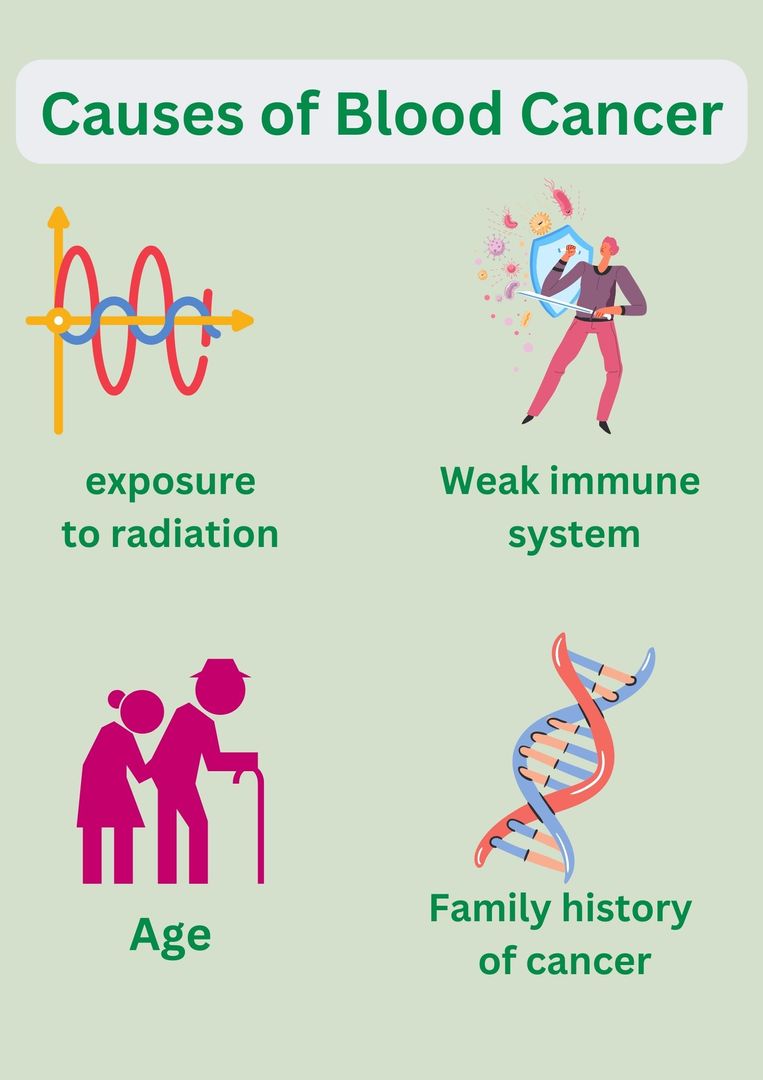
The exact cause of blood cancer is unknown, but there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing it. These factors include:
- Exposure to radiation or certain chemicals
- Family history of blood cancer
- Certain genetic disorders
- Weakened immune system
- Age (most cases occur in people over 60 years old)
What Are the Symptoms of Blood Cancer?

The symptoms of blood cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weight loss
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Pain in the bones or joints
Are you experiencing any of these symptoms?
Then hurry up! It is important to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Take charge of your health and your life. Contact us today!
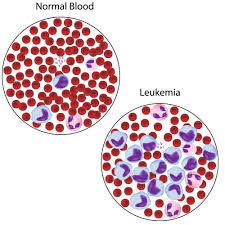
Types of blood Cancer
These are the main types of blood cancer, each with its own subtypes and variations.
Type | Details |
Leukemia
|
|
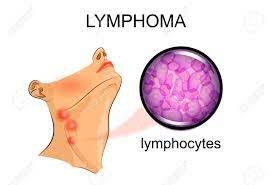
Lymphoma
|
|
Multiple myeloma
|
|
Myelodysplastic syndromes
|
|
Myeloproliferative neoplasms
|
|
If you have concerns about your health it's time to know more about blood cancer!
Your well-being is our priority - call us to book your appointment today
Diagnosis of blood Cancer
Diagnosing blood cancer typically involves a combination of medical tests and procedures to determine the type and extent of cancer. Here are some common diagnostic methods used for blood cancer:
Let us help you to know what is required to diagnose blood cancer!
| Test and Procedure | Detail |
Blood tests
|
|
Biopsy
|
|
Imaging tests
|
|
Flow cytometry
|
|
Genetic testing
|
|
If blood cancer is diagnosed, additional tests may be needed to determine the cancer stage and the best course of treatment. Working closely with a medical team to develop a treatment plan that meets your individual needs and preferences is essential.
Take the first step to recovery. Get in touch with us for your treatment.
How Is blood Cancer Treated?
Like every problem, the problem of blood cancer also comes with solutions!
So, why not focus on solutions instead!
The cure for blood cancer depends on several factors, such as the type and stage of the disease, the patient's age and overall health, and preferences.
According to Sean Marchese, a registered nurse at The Mesothelioma Center with a background in oncology clinical trials, a master's in medical sciences, and over 20 years of patient care experience,
“The stage of blood cancer can affect treatment options, as more advanced cancer may require more aggressive treatments such as chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation.”
Some common treatments include:

- Chemotherapy- Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. The drugs are designed to target and destroy rapidly dividing cells, which include cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be used to treat a variety of cancers, including blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
- Radiation therapy- Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. The radiation can be delivered externally, using a machine that directs beams of radiation at cancer from outside the body, or internally, by placing a radioactive source inside the body near the tumor. Radiation therapy can be used to treat a variety of cancers, including blood cancers such as lymphoma and leukemia. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments such as chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation.
- Stem cell transplant- A stem cell transplant is a medical procedure used to treat certain blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. It involves the transplantation of healthy stem cells into a patient's body to replace damaged or diseased cells.
- Targeted therapy- Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to specifically target cancer cells. Unlike chemotherapy, which can also damage healthy cells, targeted therapy drugs are designed to interact with specific molecules or proteins that are found in cancer cells. By targeting these specific molecules or proteins, targeted therapy can help slow down or stop the growth of cancer cells, while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Targeted therapy can be used on its own or in combination with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.

- Immunotherapy- Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. The immune system is the body's natural defense mechanism against infection and disease, and it is also capable of recognizing and attacking cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells or target specific molecules or proteins in cancer cells that help them evade the immune system. One type of immunotherapy is checkpoint inhibitors, which block proteins in cancer cells or immune cells that prevent the immune system from recognizing and attacking cancer cells. Another type is CAR-T cell therapy, which involves genetically engineering a patient's own immune cells to better target and attack cancer cells. Further talking about the new treatment, CAR-T cell therapy, Sean Marchese, says,
“CAR T-cell therapy is an immunotherapy that involves modifying a patient's T cells to attack cancer cells. It can treat certain types of blood cancer, including leukemia and lymphoma.”
The goal of treatments is to destroy the cancer cells and prevent them from spreading to other parts of the body. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary. Nowadays medical science is becoming very strong and blood cancer can be cured in many ways.
Wondering but how successful are the treatments?
Scroll down to learn more!
What is the blood Cancer treatment success rate?
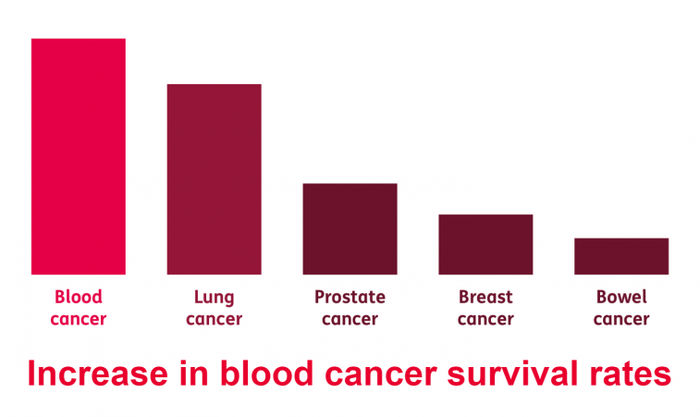
Blood cancer has a five-year survival rate of roughly 70%. Accordingly, a person with blood cancer has a 70% chance of living five years after their diagnosis compared to a person of the same age without cancer. The patient's age, general health, and the unique properties of the cancer cells are all factors that affect treatment success. Blood cancer’s survival rate has increased compared to other cancers.
Wondering if blood cancer recur after successful treatment?
According to Sean Marchese, a registered nurse at The Mesothelioma Center,
“Blood cancer can reoccur after successful treatment, and patients need regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare team to monitor for any signs of recurrence.”
As we know prevention is better than cure.
So let’s discuss how we can prevent blood cancer!
Can blood Cancer Be Prevented?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent blood cancer, but there are several things you can do to reduce your risk. These include:
- Avoiding exposure to radiation and certain chemicals
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Getting vaccinated against viruses that can increase the risk of blood cancer
- Seeking prompt treatment for any infections or illnesses
- Regularly monitoring your health and getting check-ups with your doctor
To summarize, blood cancer can be cured and caused by several factors, but there are ways to reduce your risk and seek prompt treatment if necessary.
If you are experiencing any symptoms or have concerns about your health.
Don't forget to run to your doctor it's important!
 FAQs
FAQs
- Is chemo good for blood cancer?
Chemotherapy can be an effective treatment for certain types of blood cancer, but its effectiveness depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the individual patient's health and other medical conditions.
- How successful is blood cancer treatment?
The success of blood cancer treatment can vary depending on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the age and overall health of the patient, and the treatment approach used.
Some types of blood cancer, such as certain types of leukemia and lymphoma, have a relatively high success rate with current treatments. For example, the five-year survival rate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children is over 90%, while the five-year survival rate for Hodgkin's lymphoma is around 86%.
- How long is blood cancer treatment?
The length of blood cancer treatment can vary depending on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the individual patient's response to treatment, and the treatment approach used.
For some types of blood cancer, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, treatment can last for several months to a year or more. In some cases, treatment may involve multiple cycles of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, followed by a period of close monitoring to ensure that the cancer does not return.
- Which stage of blood cancer is curable?
The possibility of cure depends on several factors such as the type of blood cancer, the location and extent of the cancer, and the individual patient's overall health and response to treatment. Stage 1 of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is mostly curable.
- What is the last treatment for blood cancer?
The last treatment for blood cancer depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the individual patient's response to treatment, and the available treatment options.
In some cases, aggressive treatments such as high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be considered as a last resort to attempt to cure cancer or achieve remission.
- How long can you live with blood cancer?
The life expectancy of someone with blood cancer can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the individual's age and overall health, and their response to treatment.
Some types of blood cancer, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) may not require immediate treatment. In these cases, patients may live for many years with cancer without experiencing significant symptoms. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) may require immediate treatment. with aggressive treatments such as chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation, patients can achieve remission and live for many years.
- How is a bone marrow transplant for leukemia done?
A bone marrow transplant for leukemia is conducted similarly to a blood transfusion; it does not require extensive surgery. In performing a bone marrow transplant for leukemia, a needle is put into a pelvic bone, to collect bone marrow cells from the donor's bloodstream.