Overview
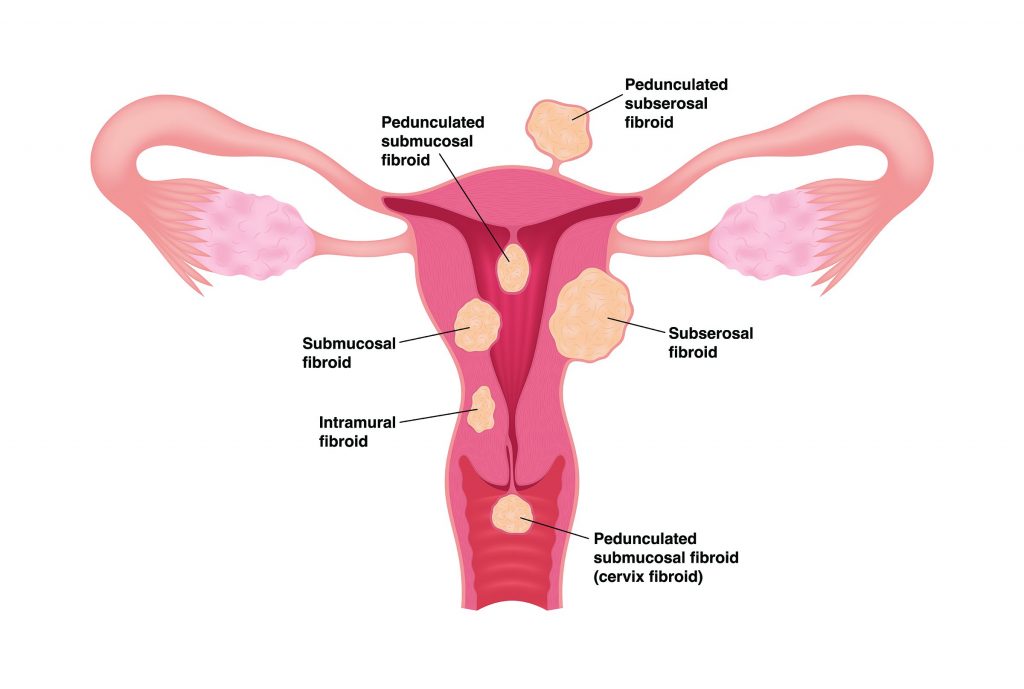
Fibroids, or uterine fibroids, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They are made up of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue and can vary in size from tiny, seed-like growths to large, bulky masses. Fibroids can be located within the wall of the uterus, protrude into the cavity of the uterus, or grow on the outer surface of the uterus. Degenerating fibroids refer to a condition in which fibroids begin to break down or degenerate. This occurs when the fibroid outgrows its blood supply, causing the tissue to die and necrotic.
Worried about fibroid degeneration during pregnancy? Book an appointment with the best gynecologists to discuss your concerns and get personalized care.
What causes uterine fibroid degeneration during pregnancy?
Uterine fibroid degeneration can occur during pregnancy due to several reasons, which can include:
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy causes significant hormonal fluctuations, particularly in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can impact fibroid growth and degeneration.
- Increased Blood Flow: The increased blood flow to the uterus during pregnancy can cause fibroids to outgrow their blood supply, leading to degeneration.
- Rapid Growth: The rapid growth of fibroids caused by pregnancy hormones can exceed the blood supply, causing the fibroid tissue to die.
- Mechanical Pressure: The expanding uterus exerts pressure on fibroids, potentially disrupting their blood supply and causing degeneration.
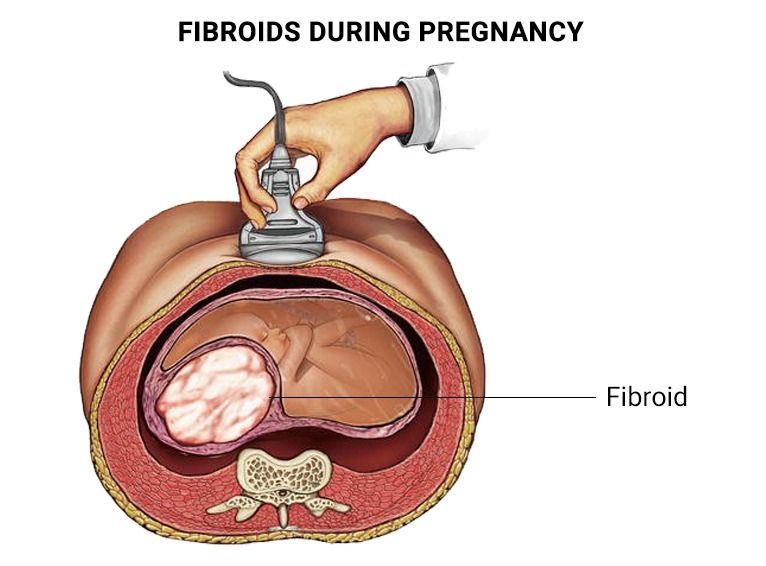
Overall, uterine fibroid degeneration during pregnancy is not uncommon and does not harm the fetus. However, it can cause pain and discomfort for the pregnant woman and may need medical attention
Likewise, at 18 to 22 weeks, the doctor advises an anomaly scan to ensure and assess the pregnancy thoroughly and determine any rare conditions.
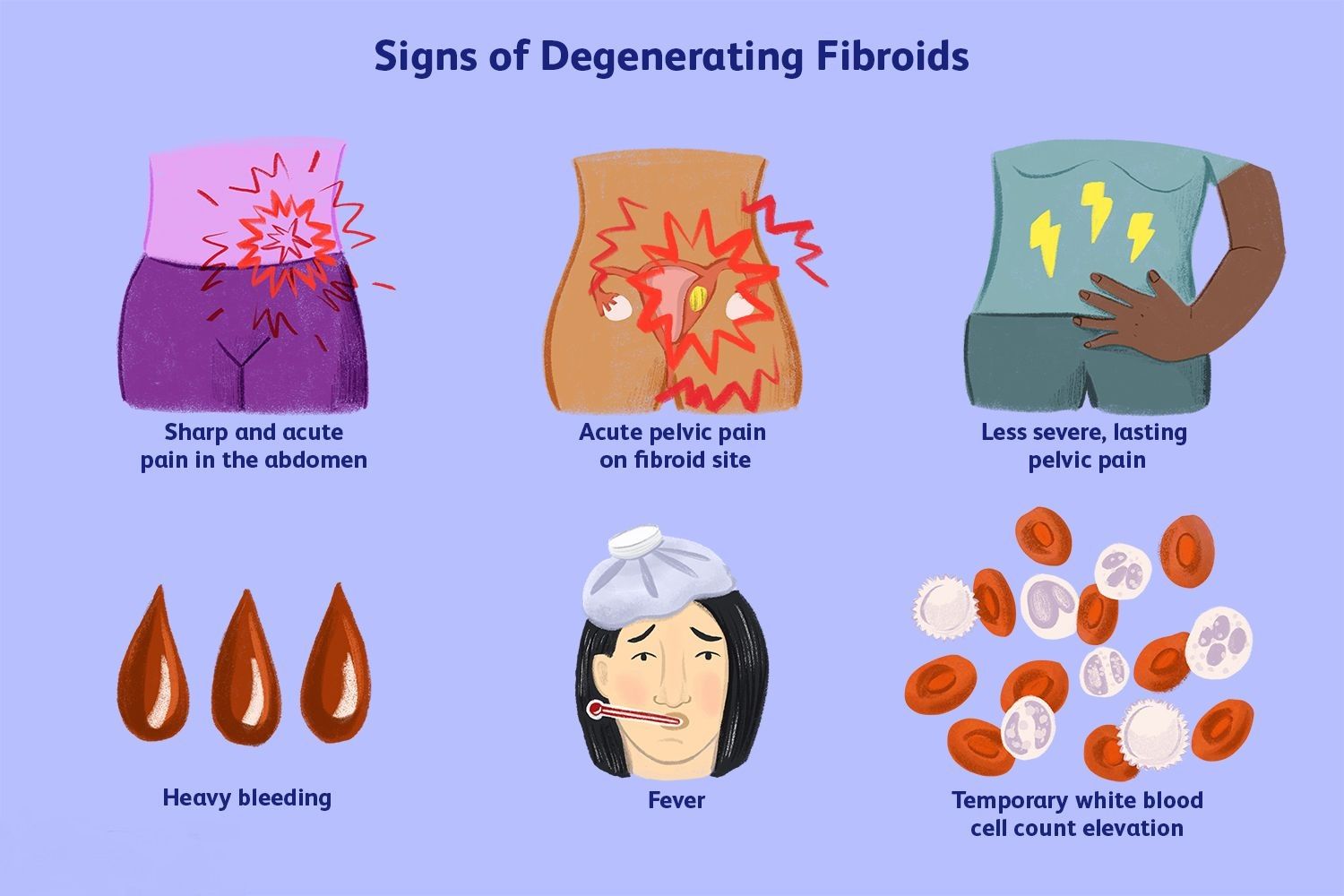
Symptoms of degenerating fibroids during pregnancy
Now you might be wondering: What happens during a degenerating fibroid during pregnancy? Understanding the process can help you prepare and manage symptoms.
What happens when there is a degenerating fibroid during pregnancy?
Women of reproductive age frequently encounter uterine fibroid. Meanwhile, 33% of fibroids may develop during the first trimester. Most of them do not alter in size while a woman is pregnant. Past studies indicate that uterine fibroids are linked to an increased rate of spontaneous miscarriage, preterm labor, placenta abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage.
- It is seen that most of the women with uterine fibroid had uneventful pregnancies. It is observed that 10%-30% of pregnant women with uterine fibroid experience difficulties and complications while giving birth. In a study involving more than 4,500 women, researchers discovered that 59% of women with fibroid experienced mild discomfort, while 11% also experienced bleeding. But, 30% of women had both bleeding and pain during their first trimester.
Dr. Swapna Chekuri, a renowned gynecologist in Hyderabad says, "Degenerating fibroids can cause significant discomfort and complications during pregnancy, but they do not lead to miscarriage directly. However, large or multiple fibroids may impact uterine function or fetal growth, indirectly increasing the risk of complications. Close monitoring and appropriate management are essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy."
- Although fibroids are common in women, they might impact fertility or pregnancy in extreme situations. Most of the time, fibroids are too small to cause obvious issues for a woman to see, so she is unaware that she has them. Larger fibroids, however, may impact the delivery or conception process. No cases have been reported, and no records from past studies show the direct impact of fibroid on the baby. But it can cause pain and discomfort for the mother. In rare cases, it can lead to complications that may need medical attention.
Can degenerate fibroid cause miscarriage?
Degenerating fibroids can cause significant pain and complications during pregnancy, but they do not typically cause miscarriage directly. However, large or multiple fibroids can potentially affect the pregnancy by causing uterine contractions or impacting the baby's growth and position. It's important to monitor and manage fibroids carefully with your healthcare provider to minimize risks.
The rate of pregnancy loss among women with uterine fibroid increased by double from 7.6% to 14%.
Though these complications are rare, a woman with fibroid needs to get in regular touch with her gynecologist/obstetrician and receive prenatal care.
Do fibroids shrink after degeneration?
Yes, fibroids can shrink after degeneration. When a fibroid degenerates, it loses its blood supply, causing the fibroid tissue to die and shrink. Timely treatment might help in stopping the degenerating fibroid from growing further. Uterine fibroid embolization is a minimally invasive treatment for curing degenerating fibroids during pregnancy.
Do you have a query about what uterine fibroid is? Then, read our blog on the success rate of pregnancy after uterine fibrosis
Your doctor will use a small catheter to administer embolic chemicals, which stop blood flow into the fibroid artery. This therapy is proven to be effective in causing the degenerative fibroid to shrink and eventually die.
If you need any further details,
References: