Overview
The journey towards gender affirmation is personal. While many transgender individuals experience immense joy through this process, some may also have concerns about their fertility potential after surgery.H owever, alongside the excitement of affirming one's true self, it's crucial to consider the potential impact on fertility.
This blog aims to address this common concern by providing a clear overview of fertility preservation options available to transgender individuals before surgery.

what exactly is fertility preservation?
Understanding Fertility Preservation
Fertility preservation involves saving or protecting reproductive cells—eggs, sperm, or embryos—to ensure the ability to have biological children in the future. This process is crucial for anyone who might undergo medical treatments or other interventions that could impair their natural fertility.
Why It Matters: This is especially important for transgender individuals considering or undergoing gender-affirming treatments. Such treatments can significantly impact fertility, making prior preservation steps essential for those who may want to have biological children later.
Let's dive into how gender-affirming treatments can affect your ability to have children in the future.
Impact of Gender-Affirming Treatments on Fertility
Gender-affirming treatments include hormone therapies and surgeries that help individuals align their physical bodies with their gender identities. These treatments can have significant implications for fertility.
Hormone Therapy:
- Transgender Women: Estrogen and anti-androgens may reduce sperm production, possibly leading to permanent infertility.
- Transgender Men: Testosterone therapy can stop menstrual cycles and may impair ovarian function, risking long-term infertility.
Surgical Interventions:
- Transgender Women: Surgeries like orchiectomy and vaginoplasty permanently end sperm production.
- Transgender Men: Procedures like hysterectomy and oophorectomy remove reproductive organs, causing irreversible infertility.
Preserving Fertility:
- Options include banking sperm or eggs before starting treatment, allowing for future reproductive possibilities.
Explore the impact of gender-affirming treatments on fertility with personalized guidance from a healthcare provider. Contact us to schedule an appointment with an expert.
Fertility Preservation Options for Transgender Men
For transgender men, gender-affirming treatments can have implications for future reproductive abilities. If biological parenthood is a consideration, it's crucial to explore fertility preservation options before embarking on treatment. Consulting with an IVF doctor can provide valuable insights into available methods such as egg or embryo freezing, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive future.
1. Sperm Banking

Sperm banking involves collecting sperm samples through ejaculation, which are then analyzed for quality and quantity. The viable sperm are frozen using cryogenic techniques and can be stored indefinitely for future use in assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI).
Pros | Cons |
| Accessibility: Easy to find and a well-known method. | Cost: The whole process, including storage, can be expensive. |
| Effectiveness: Works well with assisted reproductive technologies, offering high success rates. | Emotional and Physical Demand: This can be tough, especially if you are on hormone therapy. |
| Flexibility: Sperm can be stored whenever you choose, giving you much control over family planning. | Delay in Transition: You need to stop hormone therapy temporarily to collect sperm, which can set back other transition steps. |
2. Testicular Tissue Cryopreservation
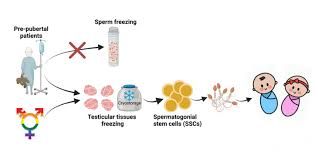
This less common method involves freezing testicular tissue that still contains stem cells capable of producing sperm. This tissue can potentially be reimplanted or used to extract sperm directly in a lab setting in the future, although these applications are still under development.
Pros | Cons |
| Innovative: Uses the latest research to help preserve fertility. | Experimental Stage: Still new and not widely available. |
| Potential for Future Use: This could lead to new ways to use sperm for having children later on. | Uncertain Success: It’s unsure if sperm from thawed tissue will work well. |
| Preserve More Options: Offers more ways to keep fertility than just freezing sperm. | Limited Implementation: Not many clinics offer this, and the methods are still being perfected. |
Schedule a consultation to explore fertility preservation freezing options suited to you!
Fertility Preservation Options for Transgender Women
For transgender women, starting hormone therapy can affect their fertility. Here’s what you can do to preserve your fertility before beginning your treatment.
1. Egg Freezing (Oocyte Cryopreservation)

Pros | Cons |
| High Potential for Success: Younger women see better results due to healthier eggs. | Costly: Expensive procedures not usually covered by insurance. |
| Flexibility: Eggs can be stored for a long time, giving you flexibility for when to start a family. | Emotional and Physical Challenges: Hormone treatments and egg retrieval can be tough both physically and emotionally. |
| Technological Advances: Improved freezing methods have raised the success rates of using thawed eggs. | Hormonal Interruption: You must stop hormone treatments temporarily, which can disrupt your transition plans. |
Schedule an appointment now to learn more about embryo-freezing options!
2. Embryo Freezing
Embryo freezing involves creating embryos by fertilizing eggs with sperm (either from a partner or a donor).
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved as in egg freezing. They are then fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish to form embryos.
- Embryo Culture: The embryos are cultured and monitored for development.
- Cryopreservation: Healthy embryos are frozen using vitrification.
Pros | Cons |
| Higher Success Rates: Embryos have better survival rates in freezing, leading to more successful future pregnancies. | Need for Sperm: Requires sperm from a partner or donor, adding extra steps and costs. |
| Long-Term Storage: Can be stored for many years, offering flexibility for future family planning. | Complex Process: There are more steps than egg freezing, including retrieval and fertilization. |
| Technological Advances: Improved freezing techniques increase the chances of later success. | Higher Costs: More expensive than just freezing eggs because of the additional fertilization and handling processes. |
- Success Rates: Success rates for frozen embryo transfer (FET) typically fall between 40% to 60%, although according to studies, these figures can change over time as technology and techniques improve.
- Considerations:
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Discuss legal and parental rights for embryo ownership and use.
- Cost: Like egg freezing, IVF and embryo freezing can be costly.
3. Ovarian Tissue Freezing
- A newer option is where ovarian tissue is removed and frozen. This tissue can potentially be reimplanted later to restore fertility, though this technology is still under study.
Conclusion
We’ve covered key fertility preservation methods for transgender individuals in this blog, including sperm banking, egg freezing, and embryo freezing. Each method allows you to consider having biological children even after gender-affirming treatments.
Transitioning is deeply personal, and deciding to preserve fertility is a significant step. It ensures you keep your options open for the future.
Reference:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9496568/
https://fertility.womenandinfants.org/treatment/fertility-preservation/transgender-fertility
https://www.ivi.uk/blog/fertility-preservation-for-transgender-men-and-women/
FAQs
- Is fertility preservation right for me?
Think about whether you want biological kids, your health, and age, and how treatment might affect your ability to have children.
- What are the different fertility preservation options available?
The main methods are sperm banking, egg freezing, embryo freezing, and freezing of reproductive tissues.
- What are the success rates of these procedures?
Success depends on the method and personal details; freezing embryos usually works best, followed by eggs and sperm.
- What are the risks and side effects associated with each method?
Risks include side effects from hormones, potential complications from procedures, and emotional stress.
- How do I choose the right fertility preservation option for me?
It’s important to talk to a doctor who knows about fertility and transgender health to find the best option.
- How much does fertility preservation cost?
The cost varies, usually several thousand dollars, and insurance often doesn’t cover it.
- What are the next steps after fertility preservation?
Keep track of your stored materials, plan when you might want to use them and think about your future family plans.