Overview
Hormone therapy for transgender youth is a medical intervention that helps align their physical appearance with their gender identity. This treatment includes puberty blockers, which prevent the onset of secondary sexual characteristics that the individual may not be comfortable with.
The goal of hormone therapy for transgender youth is to align their physical characteristics to their gender identity. Many researchers have been making cases to make this therapy available for adolescents and young adults, rather than wait for them to become older.
Early intervention has shown a significant reduction in depression and other mental health issues that come with gender dysphoria.
Transgender men are those who are born as women but identify as men, while transgender women are those who are born as men but identify as women.
How Common and Popular Is HRT For Transgender Youth?
Statistics on Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) use among transgender youth, including those considering or undergoing transgender surgery, are evolving, but recent studies show a growing interest. A 2022 survey found nearly 60% of transgender and gender-nonconforming youth aged 13-17 considered or started gender-affirming hormones. Another study noted a doubling in hormone therapy initiation rates among transgender youth from 2016 to 2020.
Does Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth Work?

Isn’t this the most critical question?
The short answer is—yes it does.
Are you curious to know just how does it work?
Well, feminizing hormone therapy produces physical characteristics caused by female hormones in women. These are called secondary sex characteristics. The objective of this treatment is to block the production of testosterone.
Masculinizing hormone treatment, on the other hand, produces physical changes caused by male hormones in men during puberty. In this case, estrogen production is reduced.
Hormone therapy, when utilized appropriately and under proper medical supervision, can be a highly effective intervention for transgender youth. It alleviates gender dysphoria, enhances physical congruence with desired gender, and improves mental and emotional well-being. However, it's crucial to remember that HRT is a personal choice requiring informed consent and individualized assessments by medical professionals.
Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth (Transmen)
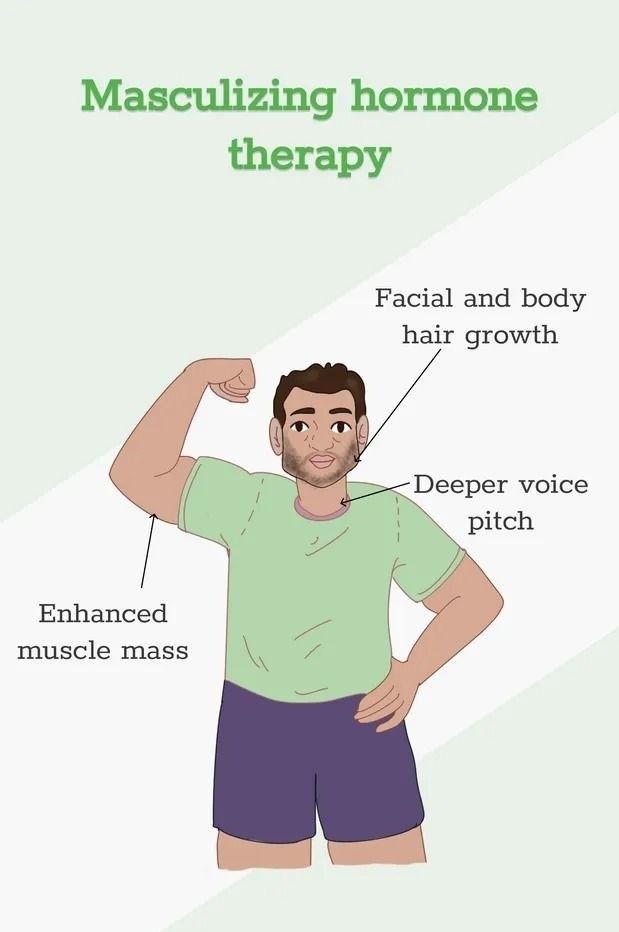
Testosterone is the hormone given to transmen. This therapy is also called gender-affirming hormone therapy. Testosterone triggers physical changes seen in males during puberty. It encourages the appearance of secondary sex characteristics like:
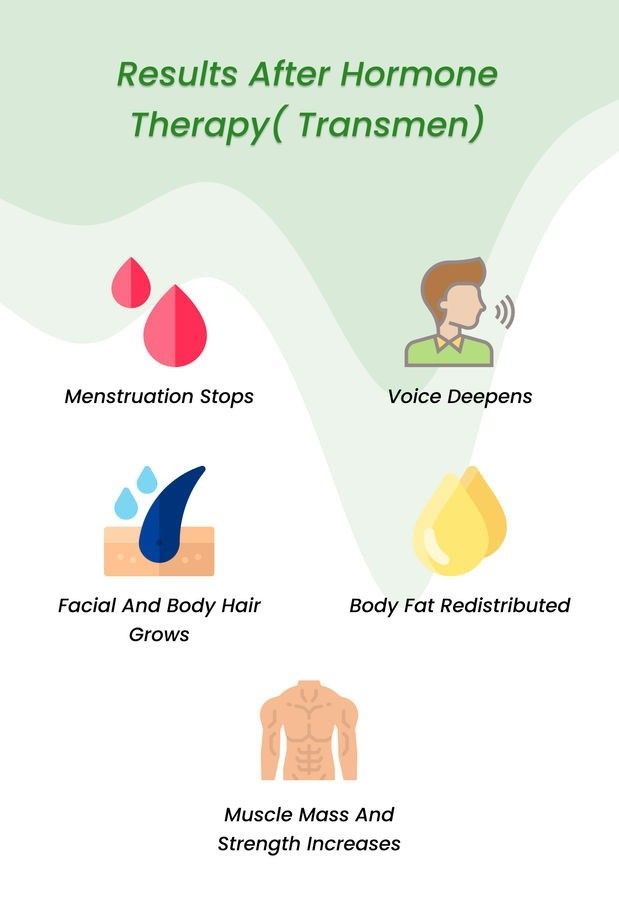
Physical Changes:
- Masculinization: Testosterone, the primary hormone used in transmen's HRT, triggers various masculinizing changes. These include:
- Deepening voice: Vocal cords thicken, resulting in a lower pitch.
- Facial hair growth: Increased facial and body hair growth.
- Muscle growth and redistribution: Increased muscle mass and redistribution of fat, leading to a more masculine physique.
- Clitoral enlargement: The clitoris may enlarge and adopt a more phallic appearance.
- Menstrual suppression: Testosterone typically suppresses menstruation over time.
Emotional and Psychological Effects:
- Reduced gender dysphoria: HRT can significantly alleviate the distress and discomfort experienced due to the incongruence between one's gender identity and physical appearance.
- Improved self-esteem and confidence: Feeling physically aligned with one's gender identity can boost self-esteem and confidence, enhancing overall well-being.
- Positive mental health outcomes: Studies show that HRT can reduce anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation in transmen, leading to improved mental health.
Considerations for Transmen:
- Age and pubertal stage: HRT protocols vary depending on whether youth have begun puberty or not. Starting during puberty suppression can prevent unwanted secondary sex characteristics associated with the assigned sex at birth.
- Dosage and monitoring: Testosterone dosage and administration methods (injections, gels, patches) depend on individual needs and are closely monitored by qualified healthcare professionals.
- Informed consent and support: Open communication and informed consent are crucial, involving a thorough understanding of potential risks and benefits. Access to supportive communities and mental health resources is also important.
Take charge of your health and your life. Contact us today!
Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth (Transwomen)
In most cases, hormone therapy for transwomen is started with a drug called Spironolactone. This medicine blocks male sex receptors and reduces the production of testosterone by the body.
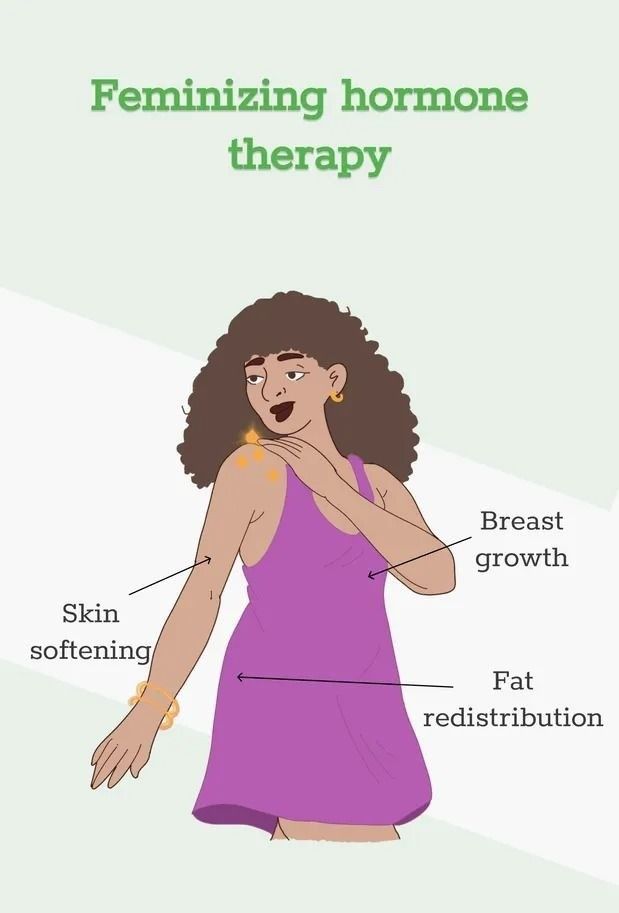
About four to eight weeks later, estrogen is started. It will trigger physical changes seen in females during puberty. Some secondary sex characteristics seen are:
Physical Changes:
- Feminization: Estrogen and progesterone, the primary hormones used in transwomen's HRT, trigger various feminizing changes. These include:
- Breast development: Growth and development of breasts.
- Softer skin and changes in body fat distribution: Skin becomes smoother and fat tends to accumulate in hips and thighs, creating a more feminine figure.
- Reduced hair growth: Facial and body hair growth may become finer and thinner.
- Menstrual cycle development: HRT can induce a menstrual cycle for some transwomen.
Emotional and Psychological Effects:
- Reduced gender dysphoria: HRT can significantly alleviate the distress and discomfort experienced due to the inconsistency between one's gender identity and physical appearance.
- Improved self-esteem and body image: Feeling physically aligned with one's gender identity can boost self-esteem and improve body image, enhancing overall well-being.
- Positive mental health outcomes: Studies suggest that HRT can reduce anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation in transwomen, leading to improved mental health.
Considerations for Transwomen:
- Age and pubertal stage: HRT protocols vary depending on whether youth have begun puberty or not. Starting before puberty allows development of secondary sex characteristics aligned with desired gender.
- Dosage and monitoring: Estrogen and progesterone dosage and administration methods (pills, patches, injections) depend on individual needs and are closely monitored by qualified healthcare professionals.
- Informed consent and support: Open communication and informed consent are crucial, involving a thorough understanding of potential risks and benefits. Access to supportive communities and mental health resources is also important.
Eligibility Criteria
Are you wondering how do you come to know if you fulfil all the criteria to receive hormone therapy?
Well, the best person to guide you through this process is your medical health professional.
The vetting process before commencing hormone therapy is quite stringent.

- A diagnosis of frequent gender dysphoria by a mental health professional
- The presence of social problems that require one’s appearance to match their gender identity
- No existing medical or psychological problems
- The youth should be capable of giving consent. If they’re not an adult, the parents’ consent is required.
Benefits and Risks of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth

As there is no rose without thorns there are no benefits without risks!
While hormone therapy for transgenders has many benefits, it also carries some significant risks.
| BENEFITS | RISKS |
|
|
How to Prepare for the Procedure?
‘Knowledge is the best weapon,’ is a popular adage. And this holds true while preparing for hormone therapy as well.
The treatment can sound daunting, given the numerous changes it will affect in your body. However, you can assuage your concerns by knowing a little bit about how to prepare for this procedure.

1. Thorough medical history: This helps the doctor understand your overall health and identify any potential contraindications for HRT. It includes reviewing allergies, past surgeries, medications, family history of medical conditions, and any existing health concerns.
2. Lab tests: A Complete Blood Count (CBC) assesses overall blood health. Testosterone/estrogen levels are crucial for understanding baseline hormone levels and determining the right therapy. Other tests like liver function tests, lipid panels, and bone density scans might be necessary depending on individual factors.
3. Screening for other diseases: Certain conditions like untreated sexually transmitted infections or uncontrolled diabetes can impact HRT effectiveness and safety. Therefore, screening for relevant diseases is crucial.
4. Mental health assessment: An assessment by a mental health professional plays a vital role in preparing for HRT. This includes:
- Gender dysphoria diagnosis: A qualified professional can assess the presence and severity of gender dysphoria to ensure HRT is the right course of action.
- Mental Health Evaluation: It's vital to explore existing conditions like anxiety or depression before Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT). HRT might interact with medications or worsen existing symptoms.
- Social Impact Assessment: Discussing potential social challenges and adjustments during transition is essential. This helps individuals prepare and build supportive networks.
Steps and Procedures Involved in Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth

Now that you know how your journey will start off, let’s delve a little deeper into the steps of this treatment.
The procedure varies slightly for men and women, and we have brought you all the details.
For Transmen
| Step 1: Diagnosis and Assessment |
|
| Step 2: Low-dose Testosterone |
|
| Step 3: Increase in Testosterone Dose |
|
All these steps are conducted as outpatient procedures and require no hospital stay.
For Transwomen
| Step 1: Diagnosis and Assessment |
|
| Step 2: Spironolactone |
|
| Step 3: Estrogen |
|
Take the first step to recovery. Get in touch with us for your treatment.
What to Expect After the Procedure?
Okay, the procedure is done! What to expect next?
Since this is an outpatient procedure, you don’t require taking many precautions. In case you have opted for taking hormone shots, you might be advised to avoid driving for a few hours.
You might also feel slightly dizzy for a few hours, but this is transient. Other than that, you can continue your daily activities without any hitches. Even after getting hormone therapy you may have other surgeries like body contouring, top surgeries etc.
Side Effects of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth
Hormone therapy can have several side effects, which vary depending on if you’re a transman or a transwoman.
MTF Hormone Therapy
With hormone therapy for transgender women, you might experience the following side effects over the years:
- Breast tenderness and development: This is usually a desired effect, but early stages can involve swelling and discomfort.
- Mood swings and emotional changes: Estrogen and progesterone can impact mood, potentially causing irritability, anxiety, or depression.
- Blood clots: There's a slightly increased risk of blood clots, especially for smokers and those with a family history.
- Weight gain and fat redistribution: Fat may shift to hips and thighs, mimicking a feminine figure, but overall weight gain can also occur.
- Headaches and nausea: These are typically mild and temporary, but can be bothersome for some individuals.
- Skin changes: Acne, oily skin, and increased sweating are potential effects related to hormonal changes.
- Sleep disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep may occur in some people.
- Vaginal changes: Dryness, discharge, and itching can occur due to decreased estrogen production in the vagina.
FTM Hormone Therapy
As a transman, you might have to keep an eye out for the following set of side effects:
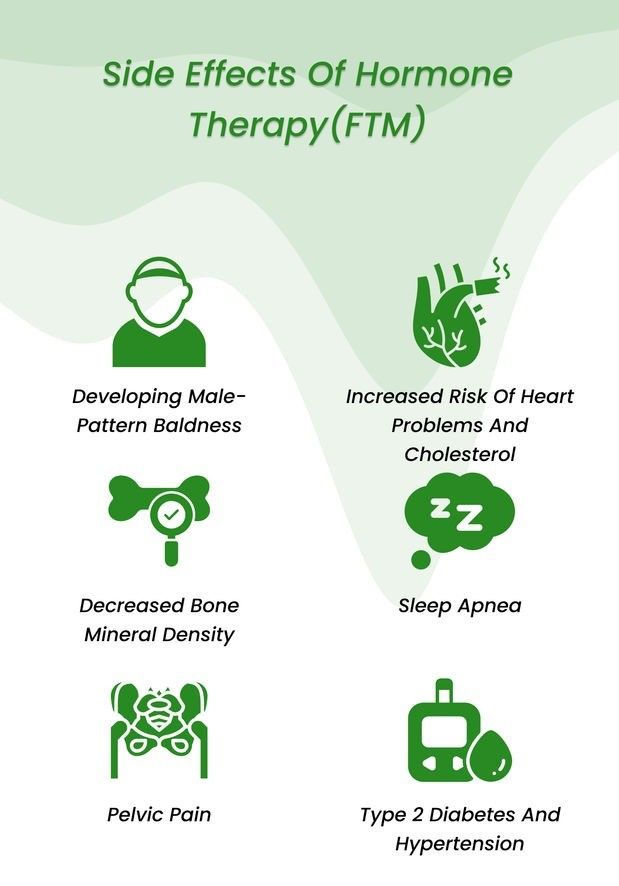
- Acne: Testosterone can increase oil production and trigger acne breakouts, especially in teenagers and young adults.
- Weight gain: Muscle mass might increase, but fat distribution can shift, leading to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
- Mood swings and emotional changes: Testosterone fluctuations can affect mood, causing irritability, anxiety, or depression.
- Sleep disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep is a possibility, especially during the initial adjustment period.
- Skin changes: Increased sweating and oily skin are common due to hormonal changes.
- Hair loss: Some individuals experience male-pattern hair loss, similar to cisgender men.
- Headaches and nausea: These are typically mild and temporary, but can be bothersome for some people.
- Red blood cell overproduction: Testosterone can lead to an increase in red blood cells, potentially thickening the blood and increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Changes in sexual function: Decreased erectile function or libido can occur due to hormonal changes.
- Pelvic pain: Some individuals experience pelvic pain or discomfort, particularly during the early stages of testosterone use. This can be due to changes in the reproductive organs or increased sensitivity.
Tensed after reading this?
Let’s reduce your tension by discussing the amazing success rates got from this therapy!
Success Rates of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth
The success rates of hormone therapy depend on several factors, the most important of which is continuance.
In general, hormone therapy has an almost 100% success rate. However, the continuance rate of this treatment is about 74%. Those who started this treatment as adolescents also continued it for longer.
Okay, so you’ve started hormone therapy. But what about the most important and concerning thing, the results?
When can you expect to see results? And more importantly, what results will you see?
Life After Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth
Well, you will notice initial changes as soon as three months after the start of your treatment, regardless of whether you’re a transman or a transwoman.
Your secondary sex characteristics will start becoming visible a few months later.
For Transmen:
| Menstruation stops | Within 6 months |
| Voice deepens | In 1-2 years |
| Facial and body hair grows | In 3-5 years |
| Body fat redistributed | In 2-5 years |
| Muscle mass and strength increases | In 2-5 years |
For Transwomen:
| Breast Development | In 2-3 years |
| Fewer erections and decreased ejaculation | Within six months |
| Slower scalp hair loss | In 1-2 years |
| More body fat and reduced muscle mass | In 2-5 years |
| Less facial and body hair growth | Within 3 years |
These results might be called permanent, but they only last as long as one continues their hormone therapy.
Cost of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth
If you are planning to undergo hormone therapy, you might be eagerly waiting for this section of the article, right?
Well, the cost of hormone therapy depends on several factors, including which city you live in and which facility you get your treatment from.
On average, HRT transgender can cost anywhere from $30-$100 a month for individuals without health insurance.
The estimated cost of HRT for transgender youth in India in USD ranges from approximately $4,000 to $5,700 per year. Here's the breakdown in both INR and USD:
Category | INR Range | USD Equivalent (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
Hormones | Rs. 1,20,000 - Rs. 2,40,000 | $1,500 - $3,000 |
Injections/gels/patches | Rs. 80,000 - Rs. 1,20,000 | $1,000 - $1,500 |
Blood tests | Rs. 20,000 - Rs. 40,000 | $250 - $500 |
Doctor consultations | Rs. 40,000 - Rs. 80,000 | $500 - $1,000 |
Does Insurance Cover the Cost of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth?
Up until very recently, this treatment was not covered by medical insurance.
However, in February 2022, the Indian Government rolled out a scheme to cover this treatment under medical insurance.
Access to Gender-affirming Hormone Therapy and overall gender-affirming care depends on your location and insurance plan. Although many companies are lagging in implementing this guideline, we anticipate that most major medical insurances will include this treatment in their policies in the coming months.
What Other Treatments Can Be Used Along with Hormone Therapy for Transgender Youth?
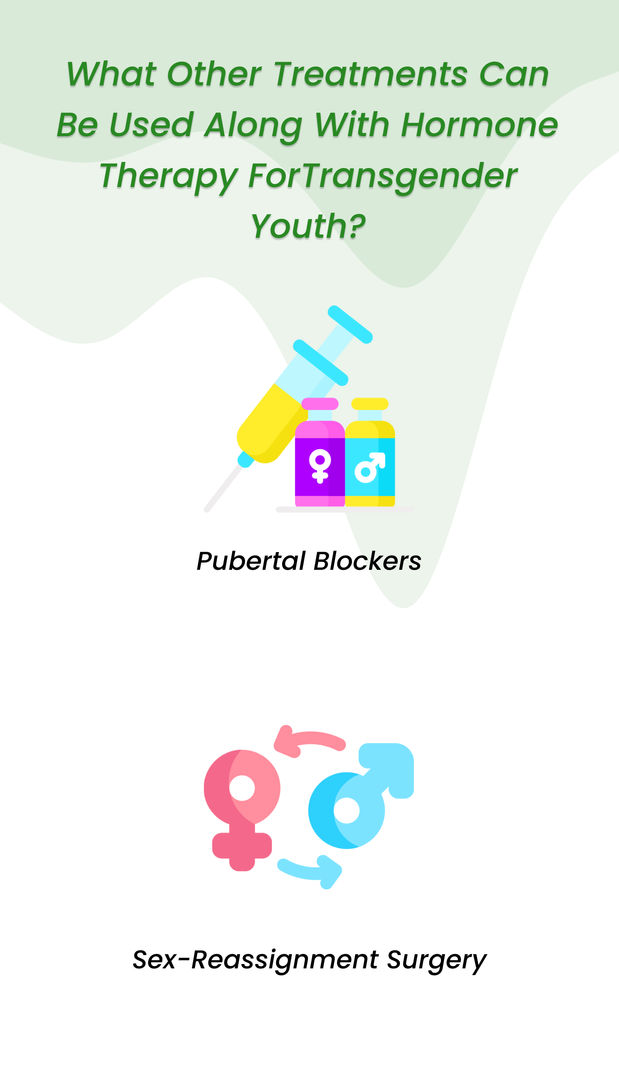
Hormone therapy is the most important treatment for treating gender dysphoria in transgender youth.
However, there are a couple of other treatments that might be used in conjunction with it.
Pubertal blockers:
- Also called Gonadotropin-releasing Analogues
- Useful in adolescents who are still undecided about their gender.
- Administered in stage two of puberty
Sex-Reassignment Surgery:
- Done in individuals who would like to have genitals that match their gender identity
- Hormone therapy is required even after the surgery.
So, what are you thinking?
It is now time to replace embarrassment and distress with confidence, pride and self-love by getting the best hormone therapy!
It is time to be the real you!
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is Transgender Hormone Therapy Reversible?
Yes, this treatment is reversible up to a certain extent if you stop it. However, some characteristics like breast development might be irreversible.
- What is the best age to start hormone treatment for transgender youth?
In general, it is advised that the individual is at least 16 years old when they start this treatment. However, pubertal blockers can be administered at the age of 14 if required.
- Do hormones help gender dysphoria?
Yes, they do. However, it is only one of the treatments for gender dysphoria. Other treatments include voice therapy and psychological therapy.
- How long does hormone therapy last?
Hormone therapy requires to be continued for the rest of your life to maintain your gender changes.