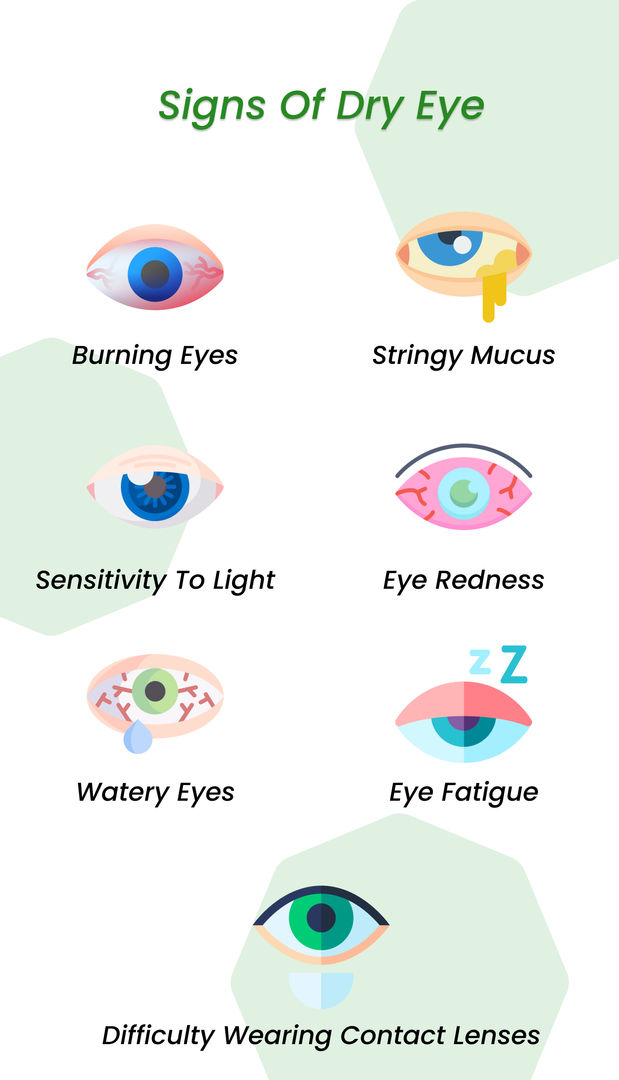
Dry eye disease is one of the most common as well as uncomfortable eye conditions. It occurs when our eyes are not sufficiently lubricated. Tears lubricate our eyes. You get dry eyes when you produce poor-quality tears or not enough tears. The lack of tears inflames and injures the eye’s surface.
There are many choices for dry eye treatment. Dry eye remedies include over-the-counter eye drops and ointments. Lifestyle changes and a combination of therapies are also effective, bringing long lasting relief, but there is no permanent eye dryness treatment as this is a chronic condition.
In their efforts to find a new dry eye treatment, ophthalmologists received FDA approval for a breakthrough medicine for dry eyes. The FDA approved Tyrvaya (Oyster Point) in 2021 as the world’s first nasal spray for dry eye treatment.
More About FDA approved Tyrvaya

Oyster Point’s Tyrvaya received FDA approval in October 2021. It is an aqueous nasal spray with a highly selective cholinergic agonist. The varenicline solution in this latest treatment for dry eye syndrome binds to cholinergic receptors. The receptors increase basal tear film production by activating the trigeminal parasympathetic pathway. In layman's language, Tyrvaya helps your body to create more natural tears.
The FDA approval came on the basis of the data from three clinical trials those are ONSET-1, ONSET-2, and MYSTIC. More than a thousand patients with dry eye disease participated in the trials.
Would you like to know more about the trials? Then read along till the end.
How did the experiments work?
Over 1,000 patients with dry eye illness participated in the Tyrvaya nasal spray clinical studies - ONSET-1, ONSET-2, and MYSTIC.
- The majority of patients in ONSET-1 and ONSET-2 were female (74%).
- Further, the mean age in the trials was 61 years.
- The average baseline anesthetic Schirmer's score was 5.1 mm (2.9).
- The average baseline eye dryness score (EDS) was 59.3 (SD) (21.6). Artificial tears could be used throughout the studies.
Researchers analyzed the change of anesthesia-induced Schirmer's score baseline to quantify basal tear production. It was done using calibrated filter paper to wick tears and measure tear volume. Further, researchers assessed eye dryness with the Eye Dryness Score (ESD). ESD is a visual analogue scale that patients use to judge how uncomfortable their eyes were. A lower score suggested greater symptom relief. Both the controlled adverse environment (CAE®)* and the clinic setting were used to measure the eye dryness score.
Researchers saw statistically significant changes in Tyrvaya-treated individuals at Week 4. 52% of the patients treated with Tyrvaya in the ONSET-1 study achieved a 10 mm increase in Schirmer's score from baseline. 47% of the patients in the ONSET-2 study achieved the same. On the other hand, only 14% and 28% of patients treated with a vehicle in the ONSET-1 study and the ONSET-2 study achieved a 10 mm increase in Schirmer's score from baseline.
Side effects of Tyrvaya
82% of patients reported sneezing as the most common adverse reaction to Tyrvaya. Around 5-6% of patients in the trial also had throat, nose, and cough.
Note: Doctors usually recommend taking it at an interval of 12 hours. In case you skip a dose, don’t take extra. Just take the next dose at the scheduled time. Since Tyrvaya is a nasal spray, do not shake it. The dosage your doctor prescribes depends on several factors, including the frequency and severity of your other health conditions. Taking any medication requires the advice of a doctor.
References:
https://dryeyedirectory.com/dry-eye-treatment/#medications-dry-eye
https://www.aao.org/eye-health
https://investors.oysterpointrx.com/news-releases
https://www.drugs.com/tyrvaya.html
https://www.pharmacytimes.com/