Did you know that obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease? It is the leading cause of death worldwide. According to WHO, over 2.8 million deaths occur each year due to obesity-related heart diseases. These alarming statistics highlight the urgent need to understand the connection between obesity and cardiovascular health.
What is the connection between obesity and cardiovascular disease?
Obesity is defined as having excess body fat. It can increase the risk of developing various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure, and heart failure. In fact, research shows that individuals with obesity are at a higher risk of heart-related issues, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, and heart valve problems. Moreover, obesity not only impacts physical health but also has significant emotional, social, and economic implications.
Let's read on to have a closer look at this!!
How does obesity increase the risk of cardiovascular disease?
Obese people usually have high blood pressure because they need more blood to supply oxygen and nutrients. Your body needs to exert more pressure to circulate this blood throughout the body. This gives rise to hypertension, which is a leading cause of obesity and heart attacks.

Also, obesity reduces the amount of good high-density lipoproteins' cholesterol. This is very important for removing the bad cholesterol and triglycerides that cause obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Diabetes is also another reason for heart disease caused by obesity. Obesity is a major cause of diabetes. As per the American Heart Association, 68% of people above the age of 65 who have diabetes are also diagnosed with heart diseases. Preventing diabetes can help prevent heart disease. Hence, it is very important to cure obesity, as it is a major reason behind diabetes.
The fact that obstructed sleep apnea causes a fragmented night's sleep is unpleasant enough on its own. But it also poses a risk for heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure. In reality, the researchers discovered that overweight individuals with moderate sleep apnea had an increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome, hypertension, prediabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
Don't suffer any longer, book your appointment now.
Which type of obesity is most associated with cardiovascular disease?
There is a significant relationship between obesity and heart disease. Death from cardiovascular diseases is high among individuals who are overweight or obese because of the excessive deposition of adipose tissue.
Abdominal obesity is the type of obesity that causes the most harm to people. It raises the chances of cardiovascular disease. Obesity may be linked to increased amounts of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein, diabetes, insulin resistance, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, all of which raise the chance of cardiovascular diseases and obesity heart attack.
Do not worry,
We have listed the best cardiologist and heart hospitals for better treatment and healthy life.
Does the time of weight gain impact the heart? Read below to learn more!!
How does the timing of weight gain affect cardiovascular disease risk?
The chances of developing cardiovascular disease vary depending upon the time of weight gain. Here are a few situations:
- Weight gained during childhood: Children who are overweight or fat are more likely to suffer from cardiovascular illness in later life. High blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and other risk factors can emerge in children who are obese.
- Rapid weight gain: Heart disease caused by obesity is associated with rapid weight gain during adulthood. Weight gain at a faster pace is linked to metabolic alterations that raise the chances of obesity and heart diseases.
- Yo-yo dieting, or frequent cycles of weight gain and reduction, has been linked to an increased chance of obesity and cardiovascular disease. This is believed to be the case because fluctuating weight can alter metabolism and exacerbate inflammation. Both of which can eventually lead to the onset of arterial disease.
- Cardiovascular disease risk can be raised by long-term weight gain, especially if it is followed by a rise in visceral weight or abdominal obesity. This is due to the fact that visceral fat has a high metabolic activity and can add to insulin intolerance and inflammation, both of which raise the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Can weight loss reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease?
Since obesity and heart disease are interrelated, reducing weight can significantly impact your cardiovascular health. It mostly improves the risk factors for developing cardiovascular diseases. Even weight loss such as bariatric surgery, can have positive effects on heart disease in individuals who are obese or overweight.
Even a little bit of weight loss is proven to produce many health benefits, like controlled blood pressure, cholesterol, and sugar.
Both observational studies and controlled experiments have shown a connection between weight loss and reductions in cardiovascular risk factors.
- According to studies, those who are overweight or obese who lose weight experience reductions in their blood pressure, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, inflammation, and triglyceride, cholesterol, and blood glucose levels. Those who lose weight demonstrate a substantial improvement in their type 2 diabetes and obesity, returning to non-diabetic blood glucose levels, and reaching remission.
- Weight loss reduces the BMI that stabilizes the cardiovascular risk factors. A 5% decrease in body weight is linked to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as lower levels of hyperglycemia.
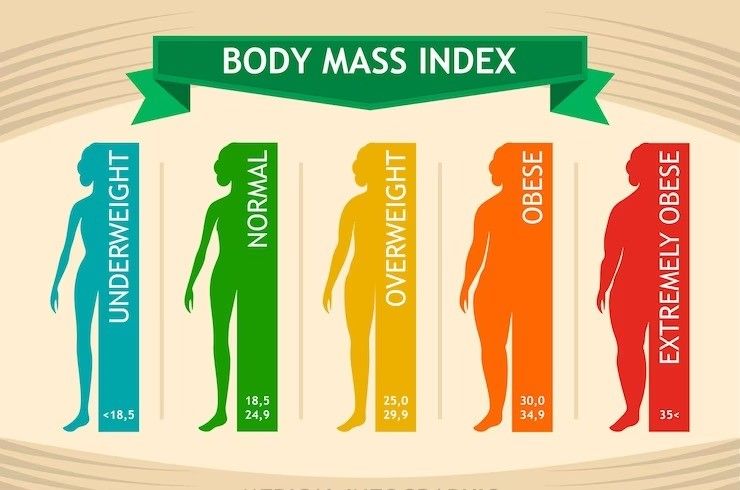
- A 5%-10% drop in body weight is linked to a decrease in intra hepatocellular lipids in the non-alcoholic fatty liver as well as a decrease in triglycerides, an increase in HDL cholesterol and a decrease in bad cholesterol.
- Greater than 15% weight loss can result in type 2 diabetes remission, particularly if diabetes has been present for a brief period of time. It can also help prevent heart failure with a maintained ejection fraction and lower cardiovascular mortality.
Diet is important for treating any kind of illness!! Let us look into the diet options for reducing the risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease!!

Is there a specific diet that can help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in obese individuals?
Yes, diets can assist obese people in lowering their chances of obesity cardiovascular disease (CVD). Here are a few examples:
- Mediterranean Diet- This diet helps in keeping the heart healthy and keeps your obesity and heart disease in check. The diet focuses on fruits, veggies, whole grains, seafood, and heart-healthy fats like olive oil. According to studies, fat people who follow this diet have a lower chance of developing CVD.

- It is advised to eat a low-fat, high-fiber diet that is rich in whole grains, five servings a day of fresh fruit and veggies, and other nutrients. The maximum quantity of salt you should consume each day is 6g (0.2 oz), as eating more than that will raise your blood pressure. One tablespoon is equal to 6g of salt.
- Include an adequate amount of unsaturated fats in the diet. Items like fish, avocados, nuts and seeds are all sources of healthy fats which increase the good cholesterol in your body to reduce the bad cholesterol in the body.
- You should make an effort to limit your intake of sugar. As diabetes is known to greatly increase your risk of obesity and heart disease.
- Low-carb diet: According to some research, a low-carb diet can help obese people with their blood pressure, blood sugar management, and blood lipid levels, which can help lower their chance of CVD.
It's crucial to remember that no diet can absolutely ensure the prevention of obesity and heart disease. To lower the chance of obesity and cardiovascular disease, a healthy diet should be combined with frequent exercise, stress management, and quitting smoking. To check the cholesterol or lipid levels, the Lipid profile test is carried out. It's available in different cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Pune, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Chennai, etc.
Take the first step to recovery. Get in touch with us for your treatment.
Lifestyle is a major cause of many diseases nowadays. Read how, by making small changes to your lifestyle, you can control the risk of obesity and heart disease.

How can lifestyle changes help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease?
- Regular physical exercise - Being more physically active improves the efficiency of your heart and circulatory system. It helps in reducing cholesterol and maintains normal blood pressure.
- The risk of obesity and heart attack is also significantly reduced because of more physical activity. Herat is a muscular organ, and exercising makes the heart muscles stronger aiding it to pump the blood more efficiently and keeping it healthy.
- Stop smoking- Smoking poses a great risk of developing atherosclerosis (furring of arteries). It is one of the major causes of coronary thrombosis in people below the age of 50. Hence, the risk of obesity cardiovascular disease is reduced which is catalyzed if you smoke too much.
- Alcohol consumption causes heart attacks and many obesity cardiovascular diseases. Reducing your alcohol consumption to 14 units a week is still acceptable. Beyond that alcohol consumption can cause obesity and heart disease.
References:
https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3250069/
https://diabetesjournals.org/
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-heart-disease/prevention/