Overview
One of the most common medical complications arising after a stroke is brain swelling, also known as cerebral edema or cerebral swelling. there are many treatments available to treat brain disease such as deep brain stimulation.
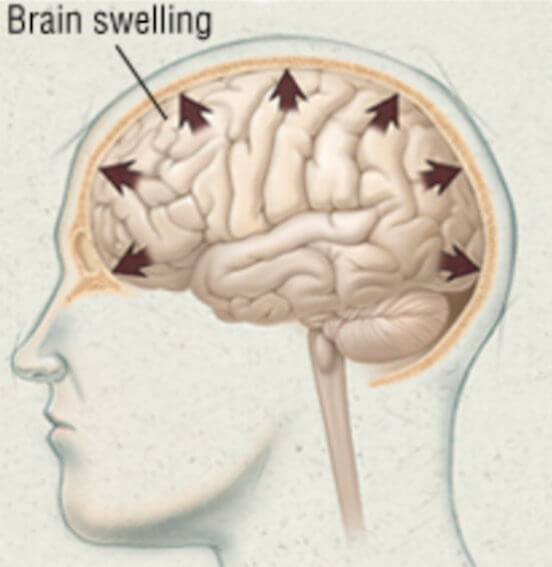
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. This happens when the brain doesn't get the oxygen and nutrients it needs, and brain cells die and cause swelling in the brain.
The swelling typically begins within hours after the stroke and can increase in intensity over the first 24 to 48 hours.

For example, when a person suffers from a stroke, a breakdown of membranes occurs within the brain, which causes proteins and electrolytes to seep into the brain tissue, leading to excess fluid accumulation.
This leads to swelling, which can be dangerous and cause further damage if left untreated.
Let's see ahead.
To know more about brain swells after a stroke, What are the causes?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide, leading to 15 million people suffering from stroke-related brain swelling each year.
About 6.5 million of these cases occur in low- and middle-income countries and account for over 12% of all deaths.
Why does the brain swell after the stroke?
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, either because a blood vessel is blocked or has burst.
When this happens, brain cells can become damaged or die, and this can cause inflammation in the brain and causes a stroke.
There are several potential causes of brain swelling after stroke, including
Damage to blood vessels: A stroke can cause damage to the blood vessels in the brain, which can lead to bleeding or the formation of a blood clot. This can cause inflammation and an accumulation of fluid in the brain, leading to swelling.
Inflammation: A stroke can also trigger an inflammatory response in the brain, which can cause swelling.
Release of chemicals: A stroke can cause the release of certain chemicals in the brain, such as cytokines and prostaglandins, which can cause fluid to accumulate in the brain and lead to swelling.
Bleeding: A brain swelling after hemorrhagic stroke, which is caused by bleeding in the brain, can also lead to cerebral edema. The bleeding can cause swelling in the brain and increase the pressure within the skull.
Infection: In some cases, cerebral edema may be caused by an infection in the brain. This can occur if bacteria or other pathogens enter the brain through a wound or the bloodstream.
Brain swelling after stroke can be a severe condition that requires prompt medical attention. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of swollen brain after stroke, it is essential to seek medical help immediately.
Are you wondering how common brain swelling is after a stroke?
Let's see!
How frequently does swelling in brain due to stroke occur?
Cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain, can occur after a stroke.
The prevalence of cerebral edema after stroke varies depending on the type of stroke and other factors, such as
- The severity of the stroke,
- The age of the patient, and
- The presence of other medical conditions.
In general, cerebral edema is more common after a hemorrhagic stroke; less than 10–20% of patients develop cerebral edema caused by brain bleeding after an ischemic stroke caused by a blockage in a blood vessel.
However, cerebral edema can occur after either type of stroke.
Cerebral edema can be a severe complication of a stroke and can lead to additional brain damage.
Early treatment is essential to reduce the risk of long-term complications and improve the chances of a full recovery.
Let us take a look at what the symptoms of brain swelling after stroke are.
What happens if the brain swells after stroke?
If the brain swells after a stroke, it can lead to additional brain damage and severe complications.
This can increase the pressure within the skull, leading to further brain damage and disrupting the blood supply to the affected area.
Symptoms of cerebral or brain edema after stroke may include
- Headache that is severe or worsening
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
- Changes in speech or language
- Changes in vision
- Changes in behavior or personality
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
According to Stephen Harrison, a senior tech officer at Researching Health stated that-
The brain's response to swelling is different from other organs in the body in a few ways. First, the brain is enclosed in a hard skull, which can make it difficult for the brain to swell. Second, the brain is relatively isolated from the rest of the body, which means that it can't get rid of swelling as easily as other organs can. Third, the brain is sensitive to changes in its environment, which can make it more susceptible to damage from swelling.
If cerebral edema is not treated promptly, it can lead to severe complications such as brain herniation, which can be life-threatening.
The amount of time it takes for brain swelling to go down after a stroke can vary, but it generally takes several weeks or longer for the swelling to go down completely. Depending on the severity of the stroke,
Let's discuss it in detail.
How long does it take for the brain swelling to go down after a stroke?
The length of time it takes for brain swelling to go down after a stroke can vary depending on the severity of the stroke and the presence of any other medical conditions.
In general, it can take several days to several weeks for brain swelling to resolve after a stroke.
Treatment for cerebral edema after stroke, or swelling in the brain, may include medications to reduce inflammation and swelling and measures to manage blood pressure and control blood sugar levels.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve stress on the brain.
It's essential to follow the treatment plan recommended by a doctor to reduce the risk of complications and improve the chances of a full recovery.
It's essential to follow the treatment plan recommended by a neurologist at the hospital to reduce the risk of complications and improve the chances of a full recovery. It's also important to continue with any prescribed rehabilitation or therapy to help the brain recover and regain function.
Brain swelling after stroke treatment, will depend on the individual's condition.
Scroll down to learn about it.
How do you treat brain swelling after stroke?
Brain swelling after stroke treatment depends on the cause and severity of the swelling.
Treatment may involve medications such as corticosteroids in some cases to reduce inflammation and swelling.
Other treatments may include
Fluids:
|
|
Diuretics:
|
|
Hypertonic saline:
|
|
Mannitol:
|
|
Barbiturates:
|
|
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot or to relieve pressure on the brain caused by swelling.
Surgery after brain stroke to cure brain Swelling
Surgery may sometimes be required to reduce brain swelling after stroke.
This procedure is typically performed when other methods of reducing swelling, such as medications and supportive care, have not been effective.
Surgical procedures that may be used to treat brain swelling after stroke include
Craniectomy:
|
|
Endovascular procedures:
|
|
Decompressive craniotomy
|
|
Decompressive hemicraniectomy:
|
|
| Ventricular drain placement: |
|
| Aneurysm clipping: |
|
It's important to note that these procedures are typically reserved for severe cases of brain swelling and are not always necessary. The decision to undergo surgery will depend on the individual patient's situation and the severity of their symptoms.
Pause,
Recovery must frighten you if you are diagnosed with brain swelling caused by a stroke.
Let's check out the response below.

Can you recover from swelling in brain due to stroke?
Recovery from cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain, after a stroke depends on the severity of the stroke and the individual patient. The extent of recovery after cerebral edema depends on the severity of the stroke and the amount of brain damage that has occurred.
Generally, the earlier treatment is received, the better the chances of recovery.
Treatment for cerebral edema after a stroke typically reduces swelling and controls blood pressure, as well as measures to monitor and manage the patient's condition.
Surgery may sometimes be necessary to remove blood clots or repair damaged blood vessels.
Rehabilitation is often an essential part of the recovery process after a stroke. Rehabilitation may include
- Physical therapy,
- Occupational therapy,
- Speech therapy.
And other types of treatment to help the patient regain function and independence.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the swelling and prevent further brain damage. Some people can recover from cerebral edema after a stroke with proper treatment and management. However, the recovery process can be long and challenging, and some patients may experience lasting effects such as
- Weakness,
- Numbness,
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
Recovery from a stroke can be a slow and gradual process, and the extent of recovery will depend on the severity of the stroke and the individual patient.
In some cases, full recovery may not be possible, and the patient may experience long-term disability.
You seem tense.
By asking yourself, How long can a stroke patient with brain swelling survive?
Let's read
How long can you survive with brain swelling after stroke?
The length of time that someone can survive brain swelling after stroke depends on the severity of the swelling and the underlying cause of the stroke.
In some cases, brain swelling can resolve independently with proper treatment, while in other cases, the swelling can be more severe and require more intensive treatment.
It is important to note that the outcome for a person with brain swelling after stroke can vary greatly, and some people may experience a full or nearly complete recovery.
In contrast, others may have permanent disabilities or may not survive. Early treatment and rehabilitation can be necessary to improve the chances of a good outcome.
In severe cases, brain swelling can be life-threatening and may lead to coma or death. The chances of survival can be improved with early treatment, including
- Medications to reduce swelling,
- Measures to reduce pressure in the brain,
- Monitoring the person's blood pressure and oxygen levels,
- Draining excess fluid from the brain.
If the cause of the stroke is not identified and treated, brain swelling may continue and lead to further damage complications and also reoccur.
According to Mark Lewis, a California-based health expert from Consumer Mag stated that-
Swollen brain after stroke can increase the risk of re-occurrence of stroke. The swelling can cause damage to the blood vessels in the brain, which can lead to the formation of blood clots. These clots can then travel to other parts of the brain or to other parts of the body, causing another stroke. Additionally, the swelling can cause inflammation in the brain, which can lead to the formation of scar tissue. This scar tissue can increase the risk of another stroke by blocking the flow of blood to the brain or by making the blood vessels more prone to rupture.
It is essential to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a stroke, as timely treatment can significantly improve the chances of recovery and survival.
If you need more information regarding the same!
Call today and get free Consultation!