Overview
When a zygote starts differentiating after 5 days of formation, it becomes an expanded blastocyst. The zygote differentiates into three components:
The blastocyst develops and the blastocoel cavity expands with a fluid. This fluid causes the zona pellucida to become thin. Zona pellucida is a protective layer. The degree to which the development and enlargement occurs determines how expanded the blastocyst is.
Wondering what can be the role of expanded blastocyst in pregnancy? Find out below!!
What is the role of the expanded blastocyst in embryonic development?
The expanded blastocyst plays a crucial role in embryonic development. It consists of specialized cells that develop into tissues that form the fetus and placenta. The inner cell mass forms the embryo. The trophectoderm or trophoblast develops the placenta.

The placenta provides nourishment and support to the growing embryo. The blastocoel cavity is filled with a fluid that provides a suitable environment for the development of the embryo.
Confused about how blastocyst and expanded blastocyst are different? Read on to find out!
What is the difference between early blastocyst and expanded blastocyst?
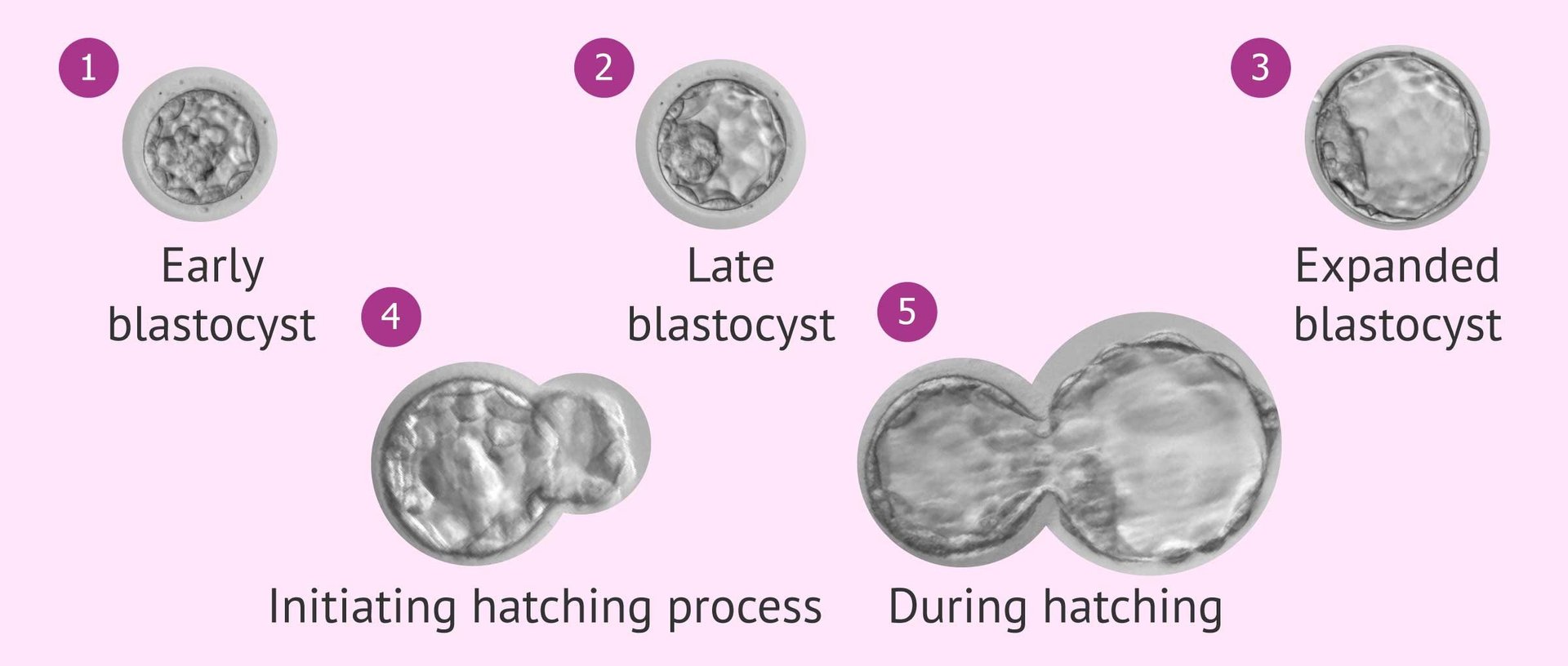
The difference between an early blastocyst and expanded blastocyst lies in their development stages and degree of expansion. An early blastocyst is when the embryo has just started to develop. It is the stage around 5 to 6 days after the fertilization. At this stage the blastocoel is smaller. The protective shell (Zona pellucida) is still intact and not thin yet.
On the other hand, an expanded blastocyst is the stage of embryo when it has developed further. It has a larger blastocoel and a thin layer of zona pellucida. The degree of expansion is often considered during embryo grading in IVF procedures.
The different stages of blastocyst expansion are:
Very early blastocyst | The blastocoel cavity just starts forming. The different cell types are not yet distinguishable. |
Expanded blastocyst | At this stage the blastocoel cavity gets fully developed. The embryo at this consist of around 100–150cells. The cells at this stage are covered with a thinner layer of zona pellucida. |
Hatched blastocyst | This is an advanced stage. The embryo emerges from zona pellucida. At this point the embryo contains more than 150 cells. |
How long does it take an expanded blastocyst to implant?
The process of implantation for an expanded blastocyst takes around 1 or 2 days. This is an important step, here the blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall to establish pregnancy.
The blastocyst undergoes several stages of development after fertilization. As a result the blastocyst expands and the embryo consists of 100 to 150 cells. During this phase the blastocyst is surrounded by zona pellucida.
Implantation usually takes place after 6 to 10 days of ovulation.During this phase the blastocyst hatches from zona pellucida. The blastocyst thus comes in direct contact with the uterine wall.After hatching the blastocyst starts getting implanted into the uterus wall.
The exact duration of implantation can vary among individuals. It depends upon various factors. The factors include:
- Quality of Blastocyst
- Receptivity of uterine lining
- The hormonal balance in the body
- Overall health condition
Learn about the impact of expanded blastocyst on implantation rates!! Continue reading to find out!
What are the chances of expanded blastocyst implantation?
The chances of successful implantation of expanded blastocyst depends on several factors as mentioned above.
In general, high quality expanded blastocysts have high chances of successful implantation.
As per a study, selecting top scoring blastocyst, based on its age, before transfer expansion and trophectoderm morphology scores have 70% chances of successful implantation.
The high quality blastocysts have well-defined inner cell masses, healthy cells and fully formed cavities. These blastocysts are graded high and have better implantation chances than low grade blastocysts.
Can an expanded blastocyst be frozen and thawed for later use?
Yes, an expanded blastocyst can be frozen and thawed for later use. Cryopreservation techniques like vitrification helps in freezing and storing blastocysts for later use.
During the procedure, the blastocysts are carefully dehydrated and preserved at low temperatures. This helps in maintaining the viability of the cells within the blastocyst.
The frozen blastocyst is thawed rapidly by warming it to use it later. The thawed blastocyst can then be used for transferring to the woman’s uterus. The blastocyst is transferred using an ART procedure called IVF.
Transferring frozen and thawed expanded blastocyst has higher success rates of implantation than fresh blastocysts.
However, the viability of blastocysts and success of the thawing process depends on factors like the quality of frozen blastocyst and cryopreservation technique used.
Below we have discussed the implications of blastocyst failure!! Continue reading further to learn about it.
What happens if an expanded blastocyst fails to implant?
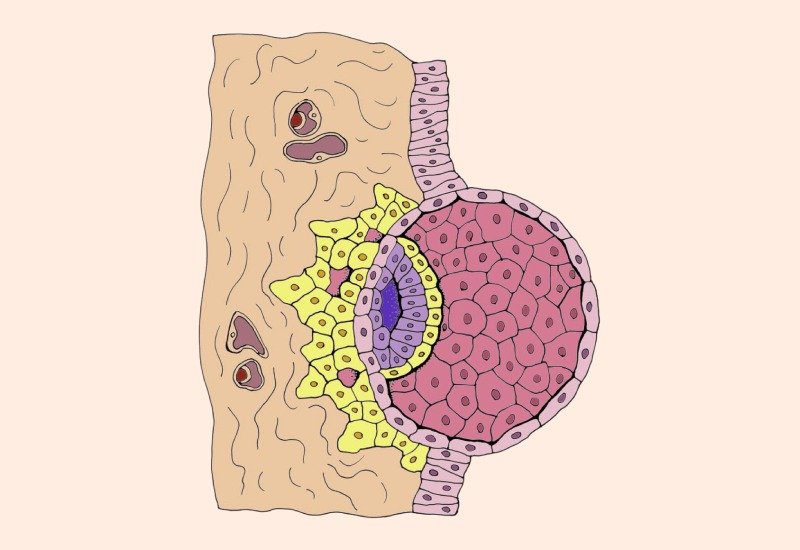
If an expanded blastocyst fails to implant it results in a failed pregnancy attempt or a negative pregnancy test.
When an expanded blastocyst fails to implant, it means that it has not attached properly to the uterine wall.
There are several factors that contribute to implantation failure. They are:
- Issues with the embryo
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Poor embryo quality
- Issues with the uterus
- Hostile environment of the uterus
- Poor receptivity of the uterus
What is the success rate of expanded blastocysts?

The success rates of expanded blastocysts depend upon various factors. Those factors include:
- Quality of embryos
- Age of the women
- Individual health issues of the couple
Using high grade blastocysts for implantation has 70% chances of successful pregnancies as compared to low grade blastocysts.
It is also of importance that you consult a reproductive specialist who can suggest personalized treatments based on your past medical history and current condition.
This will help in increasing the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between blastocyst and expanded blastocyst?
Ans. A blastocyst is an early stage embryo. It consists of a hollow ball of cells which has inner cell mass and a cavity. An expanded blastocyst is a more advanced stage. In an expanded blastocyst, the cavity has enlarged, it contains more cells, and zona pellucida has become thinner.
Q2. What grade is an expanded blastocyst?
Ans. The grade of an expanded blastocyst can range from fair to excellent. The grading depends on its overall quality and developmental characteristics.
Q3. Which is better expanded or hatching blastocyst?
Ans. An expanded blastocyst has a fully formed cavity. On the other hand, a hatching blastocyst starts to break through zona pellucida. Both have their own advantages and significance. However, the preference depends upon individual circumstances and recommendations of fertility specialists.
Q4. What is the size of an expanded blastocyst?
Ans. The size of an expanded blastocyst can vary. Generally, it measures around 100 to 200 micrometers in diameter.