Having children is the dream of almost every couple but sometimes it is not possible for the couple to have children naturally. However, treatments like IVF are the ray of hope for such couples.
Now, you must be wondering what IVF process actually is and what all it incorporates.
In general, IVF or In-Vitro fertilization is commonly known as test tube baby process.
IVF is an assisted reproductive technique, which is used when there are issues in the normal conception of a child by the couple. These issues can be the result of various health problems with either the male or female infertility counterpart or both.
In IVF, the egg (known as ovum) from the woman is taken and combined with the sperm from the male outside the body in a controlled environment (in a specialized lab). Then they are left so that the sperm can fertilize the egg. The fertilized egg (known as an embryo) is then placed in the uterus of the woman, which leads to pregnancy.
Nowadays with advancements in the IVF field, the fertilization process is carried out in a specially designed dish known as "Petri dish" in place of a test tube. The cost of IVF also differs depending upon the type you opt for and in different cities like Bangalore, Mumbai, Pune, etc.
When IVF required?
1. Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes: Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes can be the one possible reason for female infertility. The blocked fallopian tube is known as "tubal occlusion" in clinical terms.
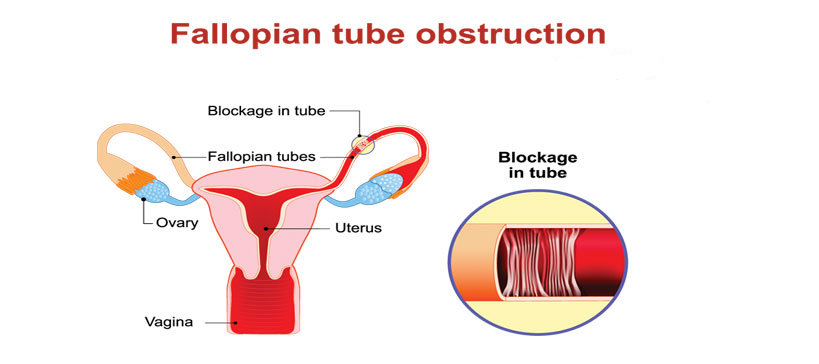
Let's first understand why fallopian tubes are important. The fallopian tubes are muscular tube-like structures that have fragile hair-like structure linings attached to them. These "hairs" work in the two directions; helping an egg to travel starting from the ovaries to the belly (uterus) and also helping the sperm to travel up from the belly.
Each fallopian tube finishes in fimbriae, which are finger-like structures. The fimbriae catch and guide an egg when the ovary discharges it. The fallopian tubes play a significant role in the fertilization process since they are the place where most eggs get fertilized.
In case any one of the fallopian tubes is harmed, for instance by a medical procedure or a disease, they can become blocked by scarred tissues.
2. Women who have had their fallopian tubes removed
As we have learnt above the role of fallopian tubes in fertility. So, in case the fallopian tubes are removed, can be because of surgery, there are no chances that a woman can conceive a child.
3. Male factor infertility including diminished sperm count or sperm motility
Low sperm count implies that the liquid (semen) discharged by a male during intercourse contains less sperm than normal.
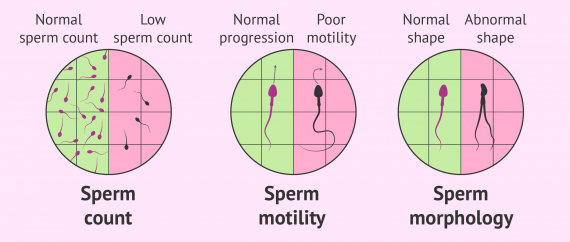
The condition of low sperm count in medical terms is known as oligospermia. A total nonappearance of sperm is called azoospermia. Sperm count is considered to be lower than normal if it is less than 15 million sperms for each millilitre of semen.
Having a low sperm count reduces the chances that the sperm will fertilize the egg, bringing about pregnancy.
On the other hand, poor sperm motility implies that sperm doesn't swim appropriately, which can prompt male infertility. Poor sperm motility is also known as asthenozoospermia. Sperm motility refers to the development and swimming of the sperm.
4. Women with ovulation issues, untimely ovarian failure, uterine fibroids
Majority cases of female infertility are the result of issues with ovulation. Without ovulation, there are no eggs to be prepared. A few signs that a female isn't ovulating normally are irregular or missing menstrual periods.
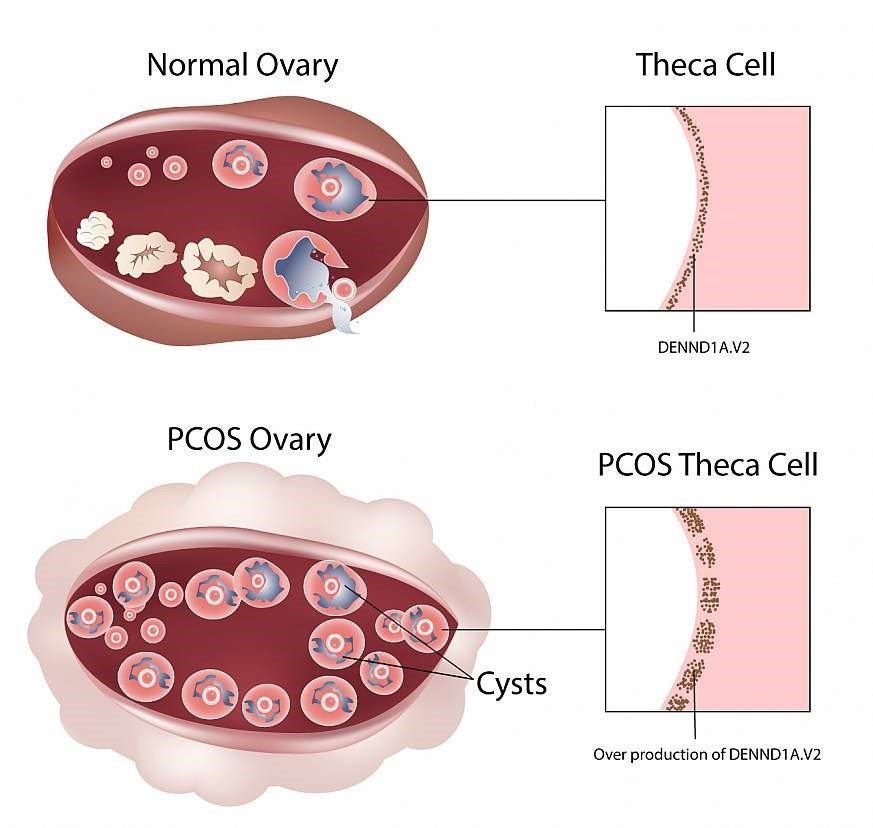
Ovulation issues are mostly the result of the polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is a hormone imbalance issue which can interrupt normal ovulation.
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) or untimely or premature ovarian failure is another reason for ovulation issues. POI happens when a woman's ovaries stop functioning normally before she is 40 years of age. POI is different from early menopause.
Though females with POI can have infrequent periods for quite a long time, they still can conceive. However, women with untimely menopause no longer have periods and are unable to conceive.
Uterine fibroids indent the endometrial cavity and endometrial polyps can disable how the covering of the uterus (endometrium) and foetus interface to bring down implantation and pregnancy chances.
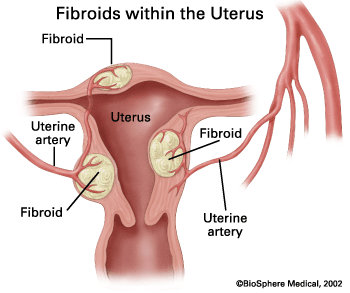
This can likewise cause unpredictable bleeding between menstrual cycles. Regular clinical check-ups are required after a half year of attempted pregnancy in women with a known history of these anomalies or a past history of bleeding between menstrual cycles.
5. People with a hereditary issue
It's important to know that there is no particular infertility gene, and neither it can be said with the prominence that every infertile person (male or female) transfers infertility to their offsprings.
In situations where infertility is passed from parents to offsprings, certain conditions can be genetic. These conditions may result in offspring suffering from infertility. Following are the few conditions:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Researches have found that issues with a female's ovary can be acquired from her mom. This incorporates PCOS, a condition that influences how their ovaries work that could prompt unpredictable periods and absence of ovulation. PCOS is an important cause for infertility for females, however, fertility treatments can help PCOS sufferers to conceive and bear a child.
- Endometriosis: It is a condition where the tissue coating the womb is present outside the belly.
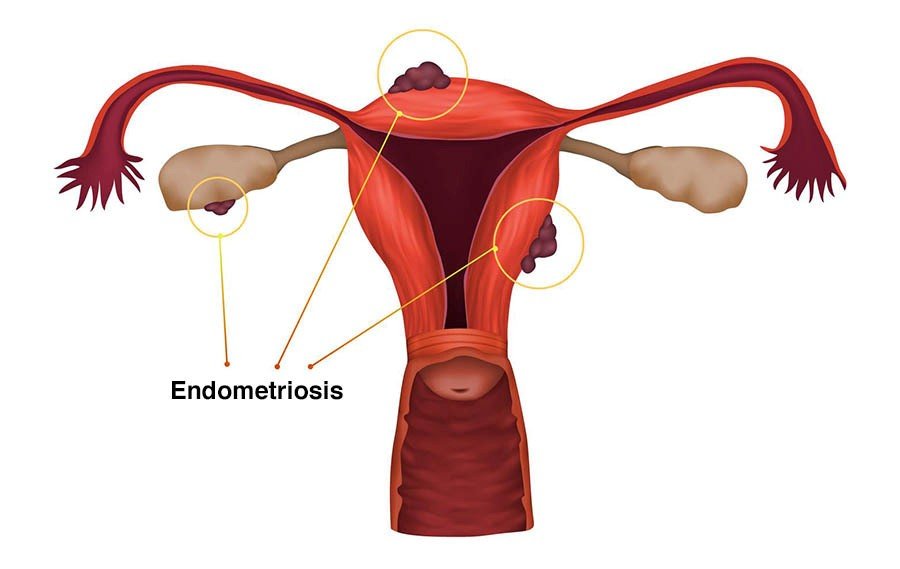
Endometriosis is another potential reason for inherited infertility. This is on the grounds that the condition can be passed from mother to daughter that may cause the daughter to face issues in conception later on in the future.
- Klinefelter's syndrome: Klinefelter's syndrome is a hereditary cause for male infertility. It is a condition whereby men have an additional X chromosome that is passed from their father. It is a major amongst the most widely recognized chromosomal disorder for men, and influences around one in every 650 men. Men suffering from Klinefelter's syndrome are prone to suffer from infertility issues.
6. Unexplained infertility
It is a type of infertility in which the causes of infertility are unknown even after utilizing all the available diagnostics.
Potential causes could be:
- The egg isn't discharged at the ideal time for fertilization to happen.
- The egg may not enter the fallopian tube.
- Sperm is unable to reach and fertilize the egg or there is implantation failure, etc.
It is progressively perceived that egg quality is of basic significance and women of advanced maternal age do not have quality eggs suitable for fertilization.
Additionally, polymorphisms in folate pathway could be one of the possible reasons.
Distorted reproductive immunology, for example, diminished maternal resistant resilience towards the developing embryo may likewise be one of the reasons.
Also, some researches have shown that epigenetic alterations in sperm can be a partial reason for unexplained infertility.
IVF process Stages
The most interesting part is to know what happens during the IVF process. So, let's see what the different stages of the IVF process are:
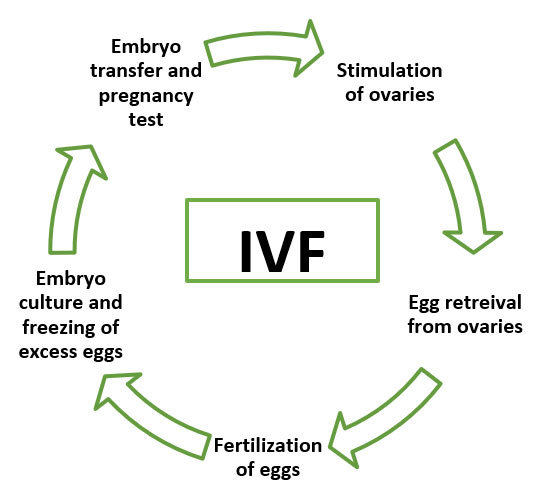
There are five essential steps in the IVF and embryo implantation process before the pregnancy test:
Side effects of IVF:
As in any medical treatment, there are certain counter effects associated with IVF.
Here we will be discussing both the common side effects that are generally encountered in IVF treatment and also the major side effects which if encountered, patient should immediately contact the doctor.
However, it is recommended not to ignore the common side effects and need to discuss them with doctor and then follow the prescription. The common side effects can be easily controlled by medications or treatment as recommended by doctor.
| Common side effects | Major side effects |
| Passing a little fluid (might be clear or blood-tinged) after the process | Heavy vaginal bleeding |
| Gentle cramping | Pelvic pain |
| Minor swelling | Blood in the urine |
| Constipation | A fever over 100.5 °F (38 °C) |
| Breast tenderness | Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) |
Side effects of fertility drugs:
According to the IVF process explained earlier, you must be aware that fertility medications are given in the initial stage. These fertility drugs can cause some of the following issues:
- Headache
- Emotional swings
- Stomach pain
- Hot flashes
- Abdominal swelling
- Ovarian hyper-incitement disorder (OHSS)
Risks in IVF
Let’s now understand the potential risks in In vitro fertilization:
High risks, typically from OHSS, incorporate the following:
- Nausea
- Decreased urinary recurrence
- Shortness of breath
- Faintness
- Extreme stomach pain and swelling
What is the success rate of IVF treatment?
After learning about IVF and other associated information, the important question that comes up is how successful the IVF process is.
The success rate of IVF process relies upon various variables such as
- conception history
- maternal age
- the reason for infertility
- lifestyle, etc.
But here we need to know that pregnancy rates are not equivalent to live birth rates. Pregnancy rate refers to the confirmed pregnancies and successful live births are known as actual live birth rates.
Talking with respect to maternal age, IVF rates are high for a woman less than 30 years of age than those above 30 years of age.
Advancements in IVF
As time passes, advancements are also making their mark in the IVF process. These advancements have resulted in new and different approaches rather than as how traditionally IVF was being carried out.
The important advanced techniques of IVF are listed below:
1. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
Basically, ICSI involves a similar procedure as IVF, with the exception that ICSI includes the immediate infusion of a solitary sperm into each egg to accomplish fertilization. ICSI is used to overcome sperm issues.
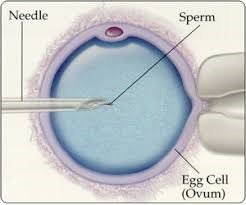
ICSI is a sort of IVF normally utilized in situations where a male has an extremely low sperm count or poor sperm motility. With standard IVF, around 100,000 sperms are placed in with each egg and kept in the incubator where the expectation is that one sperm will fertilize each egg. With ICSI a solitary sperm is infused into the egg. The entire method is the same as in IVF, the only change is how the sperm and the eggs are processed in the lab.
With ICSI, a woman has something like a one-in-three possibility of getting pregnant and having a child. If the woman's age is under 35 years, the achievement rate is near 50 per cent whereas in women who are 40 years old or more the chance of having a child is just a solitary one of every 20 with IVF utilizing her very own eggs.
2. Donor conception:
Donor conception refers to the process of having a child with the help of a donor. There are a few different ways such as donor sperm, eggs or embryos, which can be utilized in IVF processes using donors.
Let's now discuss the different cases of donor conception.
a. Donor sperm (donor insemination):
This is applicable when there is an issue with the male counterpart. Donor insemination (DI) might be utilized when:
- a male does not produce sperm,
- he does not produce normal sperm, or
- there is a high danger of a man passing on a hereditary disease or abnormality to the offspring.
Donor insemination may likewise be utilized by single women and women in same-sex relationships. The procedure of donor insemination is equivalent to artificial insemination.
b. Donor eggs:
Donor eggs are used when there is an issue with the female counterpart. Treatment with donor eggs is done if:
- a woman can't deliver eggs, or her eggs are of low quality. This may happen because of advanced maternal age (generally more than 30 years) or untimely ovarian failure (where the woman cannot produce eggs for ovulation).
- she has encountered multiple miscarriages, or there is a high danger of the woman passing on a hereditary disease or abnormality to the offspring.
In IVF with donor eggs, the procedure is the same as IVF for couple itself apart from that the donor undergoes the process of ovulation medication and egg retrieval, not the female counterpart in the couple. The egg donor undergoes hormone stimulation to deliver multiple eggs.
At the point when the eggs are mature, they are recovered and sperm from the male counterpart is added to the eggs. Two to five days later, when embryos are formed, embryo is transferred to the beneficiary woman's uterus. The beneficiary woman may take hormones in process of the embryo transfer, and for around 10 weeks after the embryo has been exchanged.
c. Donor Embryos:
Donor Embryos can be utilized if an individual or couple requires both donor sperm and donor eggs to accomplish a pregnancy. Although uncommon, a few people donate their frozen embryos that they do not need again (after IVF techniques, for instance), for use by others undergoing IVF. At the point when the beneficiary woman is ready for embryo transfer, embryos are defrosted and transferred to her uterus.
Since the donors are generally youthful, with young eggs, the success rate for IVF with donor eggs, sperm or embryo is a lot higher at up to 60 per cent.
3. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT):
GIFT was developed as a more 'normal' adaptation of IVF. Rather than fertilization happening in a petri dish in a research facility, the woman's eggs are recovered from her ovaries and embedded between two layers of sperm in fine tubing. This tubing is then transferred into one of the woman's fallopian tubes, where the egg and sperm are left to fertlize normally.
GIFT is no more regularly utilized. In any case, it is now and then utilized as an option for couples who would prefer not to utilize IVF for religious reasons, given that the woman's fallopian tubes are normal.
4. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis:
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is utilized to lessen the hazard or prevent the transmission of a hereditary malady or chromosomal irregularity from passing on to their offspring. PGD is likewise utilized for couples who have had repeated miscarriages or repeated IVF failures.
In PGD, embryos are produced through the procedure of IVF or ICSI and after that, a couple of cells are taken from the embryo and are screened for a hereditary condition. Embryos unaffected by a specific hereditary condition may then be chosen for the exchange to the woman's uterus.
5. IMSI:
Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) is a technique utilized in IVF treatment to inspect and choose sperm utilizing a high-amplification computerized imaging magnifying instrument for microinjection into the egg.
Utilizing advanced high amplification of sperm, doctors can look at the individual sperm at multiple times amplification to recognize the sperm that shows anomalies and avoid them from being utilized to fertilize the egg. The sperm that is distinguished as being normal is then utilized in the treatment strategy utilizing the ICSI technique.
With the IMSI strategy, doctors can better evaluate the structure of the sperm and prohibit the sperm with suspected irregularities from being infused into the accessible eggs.
For men with high quantities of irregular sperm and past poor results in IVF with ICSI, an upgraded choice instrument may improve the probability of treatment and better embryo advancement.
IMSI is suggested if:
- Male has low quantities of sperm.
- There is a high extent of anomalous sperms.
- There is proof of poor results with past ICSI treatment.
6. Assisted hatching:
Assisted hatching is a laboratory process that is occasionally done alongside In vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment. IVF includes blending eggs with sperm in a controlled environment in a laboratory (rather than inside a female's body). Eggs are treated as fertilized when a sperm successfully infuses into the egg.
In IVF, the fertilized eggs are monitored for 3 to 6 days as they divide and replicate and develop into embryos. The best embryo can then be placed into the woman’s uterus with expectations of helping her become pregnant or it can be frozen for later use.
While the embryo develops, it is encompassed by cells that make up a covering (zona pellucida). The embryo naturally breaks out of this shell as it develops. Sometimes, the doctor may ask the lab to soften the external shell of the embryo directly before it is put into the female's body. The expectation is that assisted hatching may help the embryo to grow and implant into the uterine wall, thereby leading to pregnancy.





