Overview
Small Head Syndrome, also known as microcephaly, is a neurological condition where a child's head is significantly smaller than expected for their age and sex. This condition often results from abnormal brain development, which can occur due to various genetic and environmental factors.
Here's what you need to know: Understanding the causes of Small Head Syndrome in adults is crucial. We'll learn the genetic and environmental factors involved.
Causes of Small Head Syndrome in adults
It can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Genetic conditions: Some genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and certain chromosomal abnormalities, can cause microcephaly.
Brain injury: Trauma to the brain, such as a head injury or stroke, can result in microcephaly.
Infections: Certain infections during pregnancy, such as rubella, cytomegalovirus, and syphilis, can cause microcephaly.
Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins or radiation during pregnancy can cause microcephaly.
Unknown causes: In some cases, the cause of microcephaly is unknown.
It is important to note that microcephaly can occur at birth (congenital) or develop after birth (acquired). In some cases, the cause of microcephaly may not be identified, and the condition may be classified as idiopathic.
The cause of Small Head Syndrome in adults is also known as Microcephaly, which can be further divided into two categories:
- Congenital Microcephaly: This condition is present at birth and can be caused by genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities. Infections, such as rubella, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasmosis, or exposure to certain toxins, such as alcohol or lead, can also cause congenital microcephaly during pregnancy.
- Acquired Microcephaly occurs after birth and can be caused by various factors, such as brain infections, brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases. Specific medical treatments, like radiation therapy or chemotherapy, can also cause Acquired Microcephaly.
There could be cases where the cause of Small Head Syndrome in adults is unknown. It's called Idiopathic Microcephaly.
Worried about small head syndrome? Schedule a consultation with the best neurosurgeons in India to get a personalized evaluation and care plan.
Symptoms of Small Head Syndrome in adults

Intellectual disability: Many adults with Microcephaly have cognitive impairments, including lower IQ and difficulties with learning problem-solving.
Developmental delays: Many adults with Microcephaly have delays in reaching developmental milestones, such as sitting, standing, and walking.
Difficulty with coordination and balance: Some adults with Microcephaly may have difficulty with fine motor skills and coordination, leading to clumsiness and an increased risk of falls.
Facial abnormalities: Some adults with Microcephaly may have distinctive facial features, such as a small forehead, a small jaw, and a small nose.
Seizures: Some adults with Microcephaly may experience seizures.
Speech difficulties: Some adults with Microcephaly may have trouble with speech or language development.
Diagnosis of Small Head Syndrome in adults
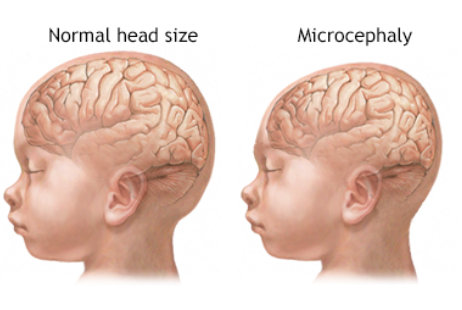
The diagnosis of Small Head Syndrome in adults begins with a physical examination where the head circumference will be measured and compared to standard measurements for age, sex, and ethnicity. If the head circumference is more than two standard deviations below the mean, it is considered Microcephaly.
Imaging tests | such as a CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound, can be used to examine the brain structure and identify any abnormalities. |
Genetic testing | can help identify any genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities causing Microcephaly. |
Neurological examination | can be used to assess cognitive function, motor skills, and reflexes. |
Blood tests | can be used to check for infections or exposure to toxins. |
Other tests | such as an EEG to evaluate the brain activity and look for seizures or a lumbar puncture to check the cerebrospinal fluid. |
Don't let small head syndrome hold you back! Learn how physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help improve your quality of life.
Treatment options for Small Head Syndrome in adults
There are several treatment options for adult patients with small head syndrome, also known as Microcephaly. These include:
Physical therapy | It can help improve muscle strength, coordination, and overall function and mobility. |
Occupational therapy | It can help patients learn to perform daily activities, such as dressing and eating, with limited abilities. |
Speech therapy | It can help patients improve communication and swallowing abilities. |
Medications | Certain medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms such as seizures or behavioral issues. |
Surgery | In some cases, surgery may be recommended to help improve the patient's condition. |
Treatment plans for Microcephaly will vary depending on the specific case and the patient's individual needs.
It is recommended to consult with neurologists in India from the best neurology hospitals to develop the best treatment plan.
Prognosis and outlook for adults with small head syndrome

The prognosis and outlook for adults with Small Head Syndrome (Microcephaly) can vary widely. It depends on the severity of the condition and any associated medical issues. Some individuals may have mild symptoms and be able to lead relatively everyday lives with the help of therapy and support. At the same time, others may have more severe symptoms and need significant help.
The life expectancy for individuals with Microcephaly can also vary widely depending on the severity of their condition and other associated medical issues. Some individuals may have an average life expectancy, while others may have a shortened lifespan.
The prognosis and outlook for adults with small head syndrome depend on the specific case and the individual's unique needs and abilities.
The small head syndrome doesn't have to limit your life! Learn about the support and resources available to help you thrive.
Coping with the physical and emotional challenges of the small head syndrome
- Seek Support: Join support groups or speak with a therapist for community and understanding.
- Learn: Educate yourself about the condition to better manage challenges.
- Stay Active: Engage in regular exercise and physical and occupational therapy.
- Be Patient: Be patient with yourself and your loved one as you navigate difficulties.
- Access Services: Utilize local government or non-profit services for financial assistance and education.
- Consider Respite Care: Use respite care to rest and recharge.
- Self-Care: Ensure you take care of your own emotional and physical well-being.
Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, a renowned Neurosurgeon states that "Genes play a crucial role in the development of Small Head Syndrome, as they can influence brain growth and head size from conception. Genetic mutations or abnormalities can disrupt normal brain development, leading to microcephaly. Understanding these genetic factors is essential for diagnosis, management, and exploring potential therapeutic interventions."
Genetic components of the small head syndrome
Small head syndrome, also known as Microcephaly, can have a genetic component. Genetic causes of Microcephaly can be inherited in different ways, such as:
Autosomal recessive inheritance | It occurs when an individual inherits two copies of a disease-causing gene, one from each parent. |
Autosomal dominant inheritance | It occurs when an individual inherits one copy of a disease-causing gene from one parent. |
X-linked recessive inheritance | It occurs when a gene located on the X chromosome causes the condition and is usually passed from mother to son. |
Mitochondrial inheritance | It occurs when a genetic disorder is caused by mutations in the DNA of the mitochondria, which is the part of the cell that generates energy. |

Many genetic causes of Microcephaly are rare, and not all cases of Microcephaly are inherited. Microcephaly can also occur due to environmental factors. For eg. infection or exposure to toxins or as a complication of other medical conditions.
A genetic evaluation by a geneticist or genetic counselor can help identify the cause of the Microcephaly and its implications on the patient and their family. The genetic assessment includes a detailed family history, a physical examination, and genetic testing such as chromosomal analysis and exome sequencing.
Knowing the cause of Microcephaly can help predict the prognosis, recurrence risk, and appropriate management options. It also allows for genetic counseling and education for the patient and their family.
Long-term effects of small head syndrome on
- Impact on physical and cognitive functioning
Small head syndrome, also known as Microcephaly, can have a wide range of effects on an individual's physical and cognitive functioning. The potential long-term impacts of Microcephaly can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition and any associated medical issues.
Physical effects
|
|
Cognitive effects
|
|
Small head syndrome can affect physical and cognitive functioning, mental health, and daily life. Learn more about it here.
- Impact on daily life and mental health
Small head syndrome, also known as Microcephaly, can significantly impact an individual's daily life and mental health. The severity of these impacts can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition and any associated medical issues.
Physical impacts |
|
Cognitive impacts |
|
Emotional impacts |
|
Mental health impacts |
|
How can small head syndrome be prevented in adults?
Prevention of Small Head Syndrome in adults can be challenging as it depends on the condition's underlying cause.
Genetic Microcephaly | Acquired Microcephaly |
Early genetic testing and counseling: For individuals with genetic microcephaly, prevention is not possible as it is inherited from parents. However, early genetic testing and counseling can help families plan for the care and support of the affected individual. | Minimizing Exposure: For individuals with acquired microcephaly, prevention is possible by avoiding or minimizing exposure to the underlying cause. For example, if the cause is a certain infection, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus, ensuring that you are vaccinated against these viruses can help prevent small head syndrome. If the cause is a brain injury, taking steps to prevent head injuries such as wearing helmets while biking or playing contact sports can help prevent small head syndrome. |
Early diagnosis and intervention can minimize the impact of the condition and improve the quality of life. Regular check-ups, monitoring of head circumference, and genetic counseling can help early detection of microcephaly.
In summary, the prevention of Small Head Syndrome in adults depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For individuals with genetic microcephaly, prevention is not possible, but early genetic testing and counseling can help families plan for the care and support of the affected individual.
For individuals with acquired microcephaly, prevention is possible by avoiding or minimizing exposure to the underlying cause. Early diagnosis and intervention can also minimize the impact of the condition and improve the quality of life.
Call to Book Your Appointment Today for more details!







