What is dysphoria and Social Dysphoria?
Dysphoria is a term used to describe feelings of discomfort, dissatisfaction, or distress. It is used in the context of mental health. To describe a range of negative emotions or experiences, such as feelings of sadness, anxiety, or agitation.

Dysphoria can take many different forms, and can be related to a wide range of experiences or situations. For example, people experience dysphoria related to their gender identity, body shape or weight, sexual experiences or desires.
Dysphoria can be a normal part of the human experience, and it may be temporary or fleeting in some cases. In some cases, dysphoria can be more persistent or intense, and may interfere with a person's ability to function in their daily life. In these cases, it is important to look for professional support or treatment to improve overall well-being.
Do you feel uncomfortable in social situations due to your gender identity?
Keep reading to learn more about social dysphoria, its symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options.
Types of Dysphoria
There are several types of dysphoria, which are generally characterised by feelings of dissatisfaction.
Here are some common types of dysphoria:
- Gender dysphoria: This is a type of dysphoria that is related to gender identity. It is an unpleasant mismatch between a person's gender identification and the sex to which they were born.

- Body dysphoria: This type of dysphoria involves a feeling of dissatisfaction with one's body. It can be related to body shape, size, or weight, and can lead to behaviours such as excessive exercise or restrictive eating, which can be easily resolved by body contour surgeries.

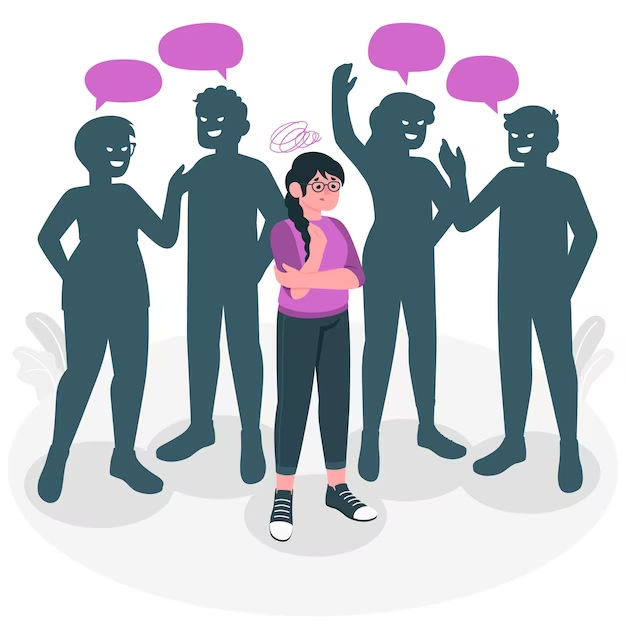
- Social dysphoria: This refers to feelings of distress in response to social situations. Also expectations that are associated with a person's gender identity. This includes using gendered restrooms or being addressed by gendered pronouns that do not align with one's gender identity.

- Sexual dysphoria: This is related to one's sexual experiences or desires. It can include a range of experiences, from discomfort during sexual activity to feelings of shame or guilt related to one's sexual orientation or preferences.

- Existential dysphoria: This involves dissatisfaction related to one's sense of purpose or meaning in life. It can manifest as a feeling of emptiness or a sense of being disconnected from others or from the world around you.

These are just a few examples of the different types of dysphoria that people may experience.
In this blog we are going to discuss Social Dysphoria in detail.
A study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health found that 44% of gender non-conforming youth reported experiencing discomfort or distress related to restroom use, which can be a common trigger for social dysphoria.
Your well-being is our priority - call us to book your appointment today
Causes and risk factors of social dysphoria
The solution lies in understanding the cause of the problem!
So, let's know what causes social dysphoria
- Gender identity incongruence: Social dysphoria is associated with gender dysphoria. This refers to discomfort experienced when an individual's gender identity does not match their gender at birth.
- Social norms and expectations: A feeling pressure to conform to traditional gender roles and expectations, like using gendered restrooms or being addressed by gendered titles.
- Discrimination and marginalisation: Transgender and gender non-conforming individuals are often subject to discrimination and marginalisation. This can contribute to social dysphoria and other mental health concerns.
- Lack of social support: A lack of support from friends, family, and can increase the risk of social dysphoria and other mental health concerns.
- Other mental health concerns: It may be more common among individuals who also struggle with other mental health concerns, such as depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
An expert at New Waters Recovery, an addiction and mental health treatment center, adds,
“It's possible that certain triggers or situations can worsen social dysphoria. For example, some people may feel more anxious or self-conscious when around a large group of people, such as in a crowded public space or during a job interview. Other individuals might become more agitated if they are asked to perform in front of an audience, have to make small talk with strangers, or attend a networking event. In addition, negative feedback from others can also be difficult for someone with social dysphoria.”
Studies have found that transgender and gender non-conforming people are more likely to experience social dysphoria. But it's important to know that social dysphoria can affect anyone who doesn't fit traditional gender norms. Getting help from mental health experts, friends and family, or transgender support groups can make a big difference.
Are you wondering if you or someone you know has social dysphoria? Look out for these symptoms.
Symptoms of Social Dysmorphia

Social dysphoria is when someone feels uncomfortable or upset. It may be because one doesn't fit in with traditional ideas of what it means to be a boy or a girl.
Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Feeling uneasy or distressed when people call you the gender you were assigned at birth.
- Feeling anxious or depressed because of your gender identity.
- Avoiding social situations where you might be misunderstood or misgendered.
- Feeling disconnected from your own body or from others.
- Wanting to change your body or appearance to better reflect your gender identity.
If you're experiencing social dysphoria, it's a good idea to seek help from a mental health professional or a transgender support group. They can help you find ways to cope with your feelings and improve your overall well-being.
If you suspect you have social dysphoria, it's important to speak to a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of social dysphoria
There is no specific test or consultation required to diagnose social dysphoria.
Professionals can help individuals explore their gender identity and work through any feelings of discomfort or distress that they may be experiencing.
The mental health professional may use diagnostic tools, such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). It is to test whether an individual meets the criteria for gender dysphoria or any other related mental health conditions.
It's important to note that seeking a diagnosis is a personal choice and not necessary for everyone. Some individuals may prefer to focus on their personal experience of gender and identity rather than seeking a diagnostic label. The most important thing is to prioritize one's own well-being and seek support if needed.
Diagnosed with social dysphoria?
Don't worry! There are treatments which can help! Let's explore them in detail!
Can social dysphoria be treated? How does treatment help?
Yes, social dysphoria can be treated and there are several ways to do it. These can include talking to a therapist, joining support groups, taking hormones or having surgery.

Talking to a therapist can help you explore your feelings and learn ways to manage social dysphoria. Support groups can also be helpful as they provide a safe space to connect with others who have similar experiences and can offer support and understanding.
Hormones can help you achieve physical changes that align with your gender identity. Hormone therapies can help like changes in body hair, voice, and fat distribution. Surgery, such as chest reconstruction or others can also help you achieve a physical appearance that aligns with your gender identity.
It's important to remember that treatment is individualized. Not everyone who experiences social dysphoria will need medical intervention. The most important thing is to have supportive resources and people who can help you manage your dysphoria and improve your well-being.
Take the first step to recovery. Get in touch with us for your treatment.
Social dysphoria management and treatment
Want to learn more about social dysphoria management and treatment options? Check out this helpful table.
Counselling and Therapy
|
|
Hormone Therapy
|
|
Gender-Affirming Surgery
|
|
Support Groups
|
|
Social Support
|
|
Education and Advocacy
|
|
Do not ignore social dysphoria and seek treatment as soon as possible!
Know the reasons why in the below section!
What if social dysphoria is left untreated?
Come forward and take charge of your mental health as well. Here you will know what are the impacts of social dysphoria.
Social dysphoria can have negative impacts on an individual's mental health and well-being if left untreated.
Some potential consequences of untreated social dysphoria may include:
- Increased risk of depression and anxiety: Social dysphoria can cause feelings of isolation, rejection, and shame. This can increase the risk of developing depression and anxiety.

- Difficulty maintaining relationships: Individuals with social dysphoria may struggle to connect with others. They are lacking in building relationships, which can lead to social isolation and loneliness.

- Decreased self-esteem and self-worth: Social dysphoria can cause individuals to feel inadequate or defective. This can lead to negative self-talk and a decrease in self-esteem and self-worth.

- Higher risk of substance abuse: Individuals with social dysphoria may turn to drugs or alcohol as a way of coping with their distress. This can lead to addiction and other health problems.

- Increased risk of self-harm and suicide: Untreated social dysphoria can cause significant emotional distress. This may lead to thoughts of self-harm or suicide.

Take charge of your health and your life. Contact us today!
Can social dysphoria be prevented? How to prevent it?
Yes we can take a step forward to prevent social dysphoria.
Scroll down to know what we can do.
Social dysphoria cannot be entirely prevented, as it is a result of societal norms and expectations that are deeply ingrained in our culture. But, there are steps that can be taken to create a more accepting and inclusive environment that can help reduce the risk of social dysphoria:

- Educate about gender diversity and the experiences of transgender and gender non-conforming individuals.
- Use gender-neutral language, such as "they/them" pronouns or "Mx." instead of gendered titles like "Mr." or "Ms."
- Advocate for policies that protect the rights of transgender and gender non-conforming individuals. These include equal access to healthcare, education, and employment.
- Create a safe and accepting environment for transgender and gender non-conforming individuals. This can be done by listening to their experiences, respecting their gender identity, and challenging transphobic attitudes and behaviours.
- Support and amplify the voices of transgender and gender non-conforming individuals by sharing their stories and promoting their visibility in media and society.
- Seek professional help and support if experiencing social dysphoria or other mental health concerns related to gender identity.
By taking these steps, individuals and communities can help create a more accepting and inclusive society for all genders, and prevent the negative impact of social dysphoria.
Confused between social dysphoria and social anxiety?
Let’s clear your confusion!
According to an expert at Live Another Day,
“Social anxiety disorder and social dysphoria are related and may partially overlap. Both include experiencing social awkwardness or pain. It's crucial to remember that social anxiety disorder is a well-known ailment, however social dysphoria is not a recognized clinical diagnosis in conventional diagnostic categories.
While social dysphoria can be used to represent a broad feeling of discomfort or unease in social interactions, social anxiety disorder often involves chronic fear or worry about social situations.”

Are you still wondering about social dysphoria? Check out these frequently asked questions:
FAQs

Q:Who can experience social dysphoria?
A:Anyone who does not conform to traditional gender norms or expectations can experience social dysphoria. Yet, transgender and gender non-conforming individuals are at higher risk.
Q:Is social dysphoria a mental illness?
A:Social dysphoria is not a mental illness, but it can contribute to mental health concerns such as anxiety and depression.
Q:How can loved ones support someone with social dysphoria?
A:Loved ones can provide support by listening to the individual's experiences and respecting their gender identity.
Q: What is transgender social contagion?
A: Transgender social contagion or social contagion transgender
refers to the spread of ideas, attitudes, behaviours, emotions, or even diseases among transgender or non-binary individuals through social networks or other forms of social influence.
Q. Does social contagion cause gender dysphoria?
A: According to studies, social contagion does not lead to gender dysphoria.