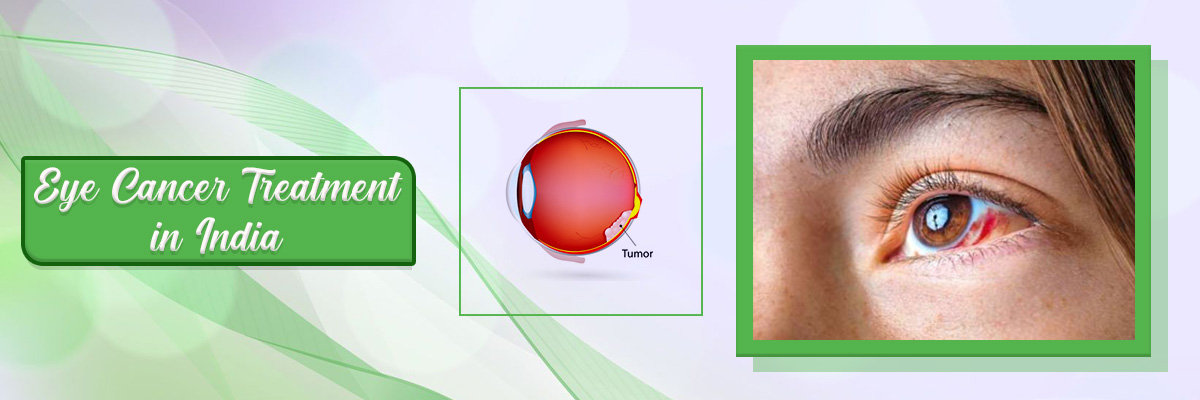
Squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid is a rare and aggressive form of thyroid cancer. It accounts for only 1% of cancers in the thyroid. It differs from other thyroid cancers, like follicular or papillary cancers. They develop from different kinds of cancers. But, squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid is different. It originates from squamous cells, which are flat and thin in structure. It occurs as a fast-growing lump in the neck. It can also spread to nearby tissues and other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid is more common in people over 50. Also, it affects females more often than men.
This type of cancer is known for its rapid progression and poor prognosis. Symptoms may include:
- A fast-growing neck mass.
- Pain.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Changes in voice.
- Possibly symptoms of local invasion such as coughing or difficulty breathing.
Genetic Factors Contributing to Thyroid Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cancers in the thyroid gland are prevalent. But, specifically squamous cell carcinoma is not very common. But still, some genetic reasons can cause carcinoma in the thyroid gland. Specific genes control the signals in our cells, and sometimes they may change. When this happens, there is a disruption of balance between cell growth and cell death. This leads to the development of tumors. Hence, it leads to squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid or other types of cancers in the thyroid.
Curious about what might increase the risk? Let's explore the factors linked to thyroid squamous cell carcinoma.
What Are the Risk Factors Associated with Thyroid Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid is a very rare type of cancer. The common risk factors associated with this are:
- Risk increases with age: Squamous cell carcinoma is often diagnosed in people above 50 years of age.
- This risk of thyroid squamous cell carcinoma is more common in females.
- Exposure to high levels of radiation increases the risk. This can be from medical treatments like radiation therapy or environmental exposure.
- Family history may be a risk factor. Certain genetic factors play a role.
- Iodine is essential for proper thyroid function. Both deficiency and excess of iodine can increase the risk of carcinoma in the thyroid.
- Some genetic conditions can increase the risk, like familial medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2).
- Some benign (non-cancerous) thyroid conditions like goitre or thyroid nodules can also be a risk factor.
How is Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Thyroid Identified?
Identifying squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid involves a combination of medical examinations and diagnostic tests. Here is how it is identified:
- Clinical evaluation by doctor: They do a physical examination and check for any lumps or abnormalities in the neck.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to visualize the thyroid and surrounding tissues.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thin needle is used to withdraw cells for analysis.
- Histological Examination: Analyzing the tissue sample for squamous cell carcinoma characteristics.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid may include:
- Surgery: It means the removal of the tumour. Sometimes a portion or the entire thyroid gland may be removed.
- Radiotherapy: Using high-dose radiation to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
- Targeted Therapy: Using drugs that specifically target cancer cells. And also minimize damage to normal cells.
- Immunotherapy: Stimulating the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
The results and outcomes of the treatment may vary. It is based on certain factors like stage, extent and overall health. You must regularly follow up with your doctor regarding your progress and make adjustments if necessary. Adhere to instructions given by your doctor and make necessary changes in your lifestyle.
FAQs:
Q1. Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread to Other Organs?
Ans. Yes, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to other organs. The likelihood of spread depends on various factors. Such as the stage of cancer and how early it is detected.
Q2. What is the Long-term Prognosis for Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Thyroid?
Ans. Early detection of squamous cell carcinoma in the thyroid can increase the chances of survival for five years after the treatment.