According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, with an estimated 10 million deaths in 2020. Cervical cancer is the second most common form of cancer in women. Therefore, the need for new and effective cancer treatments is pressing, and CAR-T therapy represents a promising new option for patients with cancer.
In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted its first approvals of CAR-T therapies for certain types of leukemia and lymphoma, making it the first gene therapy approved by the FDA. Since then, other CAR-T therapies have been approved for use in different countries, and the treatment has become widely available to patients with cancer.
If this is a treatment you’re considering, you definitely want to know how it works. Keep reading.
How do CAR T cells work in treating cancer?
CAR- T cell therapy is a revolutionary approach to cancer treatment that is helping to save lives and change how we think about cancer treatment. This new therapy involves engineering a patient's own T cells, a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in the immune system, to recognize and attack cancer cells. By extracting T cells from the patient's blood, altering them in the laboratory to express a special receptor called a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), and then infusing the modified T cells back into the patient's body, oncologists can help the T cells recognize and bind to specific proteins found on the surface of cancer cells.
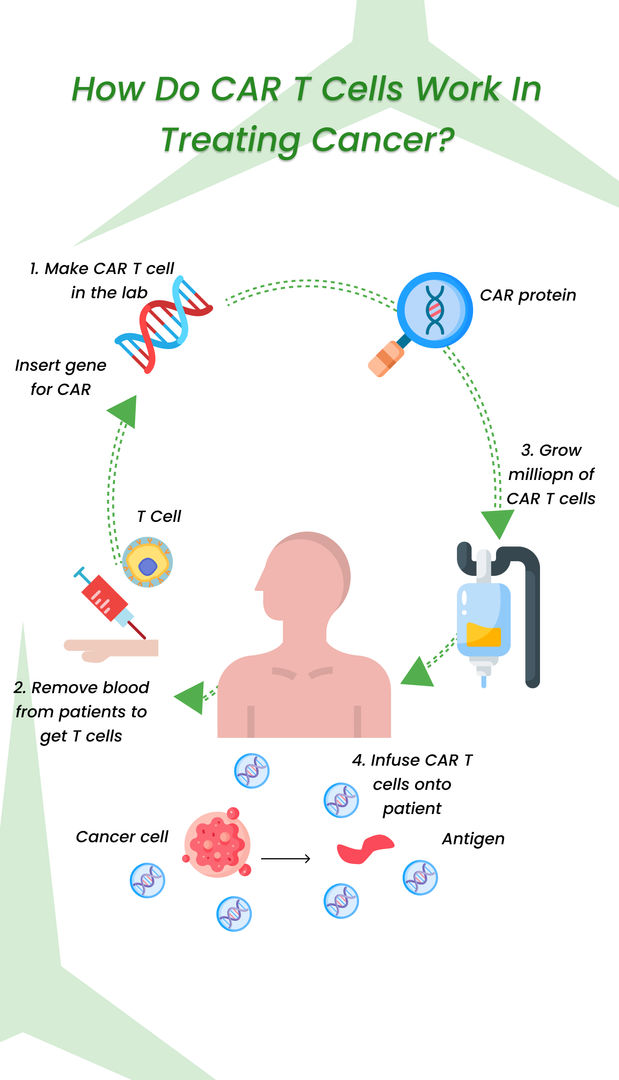
Once the T cells bind to the cancer cells, they can attack and kill them, providing a highly targeted and personalized approach to cancer treatment. Car T-cell therapy has shown great promise in treating certain blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and some solid tumors. It is a promising new treatment option for patients who have not responded to other treatments, such as chemotherapy, that have not been effective. It has already helped many patients achieve long-term remissions.
If you or a loved one are facing a cancer diagnosis, ask your doctor if the Car T-cell therapy is the suitable option for you.
Click here to find the best blood cancer hospitals in India and the cost of getting treated by the best oncologist.
How many CAR T therapies are there?
As of October 2020, several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of certain types of cancer. These include:
- Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel), was developed by Novartis and was approved in 2017 for the treatment of certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
- Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel) was developed by Kite Pharma and approved in 2017 for the treatment of certain types of lymphoma
- Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel) was developed by Juno Therapeutics and approved in 2021 for the treatment of certain types of lymphoma
- Tecartus (brexucabtagene autoleucel) was developed by Kite Pharma and approved in 2021 for the treatment of certain types of lymphoma
These therapies are only approved for the treatment of certain specific types of cancer, and they may not be suitable for all patients. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine if CAR-T T-cell therapy is an appropriate treatment option.
Let’s have a closer look at this Innovative Treatment. Here are a few insights about the success rate and response of the treatment.
What is the success rate of CAR T therapy?
The success rate of CAR T-cell therapy can vary depending on several factors, including the type of cancer being treated, the stage of treating cancer, and the patient's overall health.
Key Points | Description |
Effectiveness | CAR T-cell therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of certain types of cancer, including leukemia and lymphoma. In clinical trials, more than 80% response rates have been reported in some cases. |
Patient selection | CAR T-cell therapy is generally reserved for patients who have not responded to other treatment options and may not be suitable for all patients. |
Cure | While CAR T-cell therapy may be effective at inducing a response in cancer cells, it is not a cure for cancer. In some cases, the cancer may return after treatment with CAR T cells, and additional treatment may be necessary. |
It is always important to speak with a healthcare professional about the specific risks and potential benefits of CAR T-cell therapy or Car T treatment, as well as other treatment options that may be available. Here is a summary of some of the response rates for CAR T-cell therapy in the treatment of certain types of cancer:
Cancer Type | CAR T-Cell Product | Response Rate |
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) | Kymriah | 83% |
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | Kymriah | 50% |
Follicular lymphoma (FL) | Kymriah | 72% |
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) | Yescarta | 82% |
Large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) | Yescarta | 72% |
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | Breyanzi | 74% |
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | Tecartus | 76% |
Read ahead today to learn more and get started on your Car T-cell journey.
Also, there are certain side effects that may want to be aware about.
Side Effects of CAR T-cell Therapy
Like any medical treatment, CAR T-cell therapy can cause side effects. Some common side effects of CAR T-cell therapy include:
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS): CRS is a reaction to the body's rapid expansion of CAR T cells. It can cause fever, difficulty breathing, and low blood pressure. CRS is generally more severe in patients with higher tumor burdens.
- Neurological side effects: CAR T-cell therapy can cause neurological side effects such as confusion, difficulty speaking, or difficulty with movement. These side effects are generally reversible and resolve after the treatment is stopped.
- Infections: CAR T-cell therapy can suppress the immune system, making patients more susceptible to infections. It is important for patients to take precautions to avoid infections while undergoing treatment.
- Anemia: CAR T-cell therapy can cause a decrease in the production of red blood cells, leading to anemia.
- Low platelet count: CAR T-cell therapy can also cause a decrease in the production of platelets, which are responsible for blood clotting.
It is important to note that these side effects can be managed with supportive care, and most patients can tolerate CAR T-cell therapy. It is always important to speak with a healthcare professional about CAR T-cell therapy's specific risks and potential side effects.
Check out the cost of treatment right here.
How much do CAR-T cells cost?
The cost of CAR T-cell therapy can vary depending on several factors, including the specific CAR T-cell product used, the type of cancer being treated, and the patient's insurance coverage.
In general, CAR T-cell therapy is a costly treatment option. The list price for a single treatment with Kymriah, a CAR-T cell therapy developed by Novartis, is around $4,75,000. The price for a single treatment with Yescarta, a CAR T-cell therapy developed by Kite Pharma, is around $3,73,000.
The cost of CAR T-cell therapy can be broken down into several different categories:
- Collection and processing of the patient's T-cells
- Manufacturing of the modified T-cells
- Administration of the modified T-cells
- Other related costs may include hospitalization, medications, and other treatments.
The list price is not necessarily the price that a patient will pay for CAR T-cell therapy. Many insurance companies cover at least a portion of the cost of CAR T-cell therapy, and some manufacturers offer patient assistance programs to help patients pay for treatment. It is always important to speak with your doctor and a financial counselor to determine the out-of-pocket costs of CAR T-cell therapy.
Does insurance cover CAR-T cell therapy?
Insurance companies' coverage of CAR-T therapy can vary depending on the policy and the patient's circumstances. Some insurance companies may cover the cost of T-cell therapy, while others may not.
It is important to check with your insurance company to determine if T-cell therapy is covered under your policy. It may also be helpful to speak with a doctor or professional and a financial counselor to determine the out-of-pocket costs of T-cell therapy and to explore any potential financial assistance options that may be available.
It is also worth noting that the cost of T-cell therapy, including CAR T-cell therapy, can be high. Some manufacturers offer assistance programs to help patients pay for treatment, and it may be worth exploring these options if T-cell therapy is not covered by insurance.
Check out the free cancer treatment options with financial help for cancer patients in India.
What countries have CAR T-cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is available in several countries, including Europe, China, Australia, Singapore, and the United Kingdom. Here is a brief overview of the availability of CAR T-cell therapy in these countries:
- Europe: CAR T-cell therapy is available in several European countries, including Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands. CAR T-cell therapies that have been approved in Europe include Kymriah, Yescarta, Breyanzi, and Tecartus.
- China: CAR T-cell therapy is available in China, and several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the Chinese regulatory authorities, including Kymriah and Yescarta.
- Australia: CAR T-cell therapy is available in Australia, and several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the Australian regulatory authorities, including Kymriah, Yescarta, and Tecartus.
- Singapore: CAR T-cell therapy is available in Singapore, and several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the Singaporean regulatory authorities, including Kymriah, Yescarta, and Tecartus.
- United Kingdom: CAR T-cell therapy is available in the United Kingdom, and several CAR T-cell therapies have been approved by the UK regulatory authorities, including Kymriah, Yescarta, Breyanzi, and Tecartus.
It is important to note that the availability of CAR T-cell therapy may vary depending on the specific region within these countries, and it may not be available in all hospitals or clinics. It is always important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine if CAR T-cell therapy is an appropriate treatment option and to determine the availability of the treatment.![]()
List of hospitals in different countries that provide CAR-T cell Therapy
United States:
- Mayo Clinic
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- University of Pennsylvania
Europe:
- University of Oxford - England
- Karolinska Institute - Sweden
Asia:
- National Cancer Center - Japan
- Cancer Institute of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences - Beijing, China
- Tata Memorial Hospital- India
Is CAR T-cell therapy the same as immunotherapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy. CAR-T Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the body's immune system to fight cancer. There are several different types of immunotherapy, and CAR T-cell therapy is one of them.
Other types of immunotherapy include monoclonal antibody therapy, which uses antibodies to target and attack cancer cells, and checkpoint inhibitor therapy, which helps to "unlock" the immune system to recognize better and attack cancer cells.
Overall, immunotherapy aims to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively, which can help shrink tumors and improve patient outcomes.
Who is a candidate for CAR- T therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is typically only offered to patients with certain types of cancer that have not responded to other treatments, such as chemotherapy. It is usually only offered to patients who have been enrolled in clinical trials or meet certain treatment criteria.
Patients who may be candidates for CAR T-cell therapy include those with:
- Leukemia (such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia)
- Lymphoma (such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma or mantle cell lymphoma)
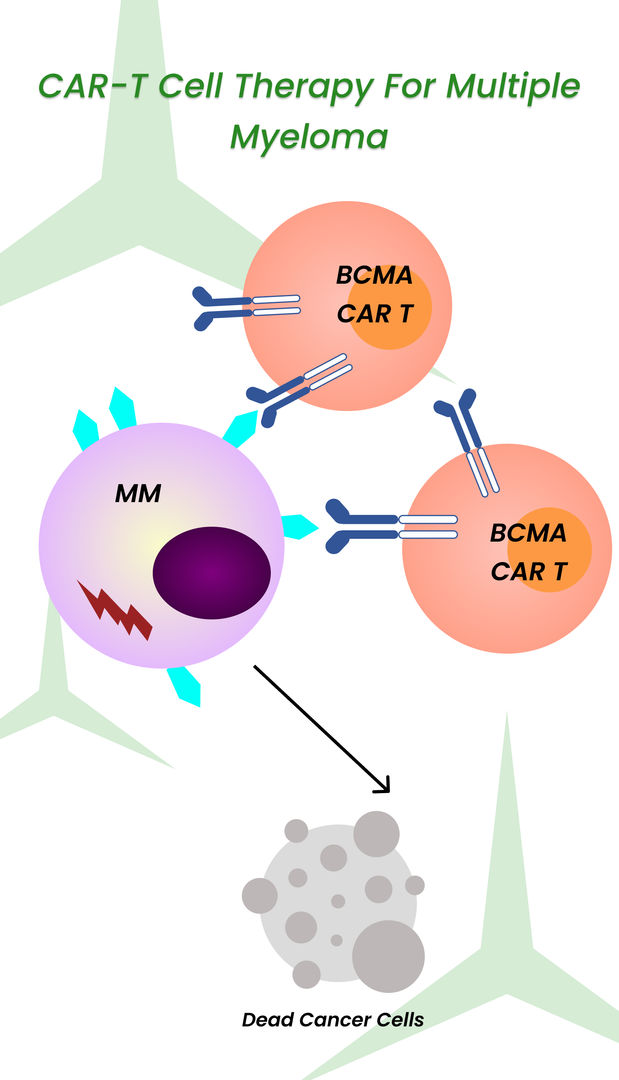
Other factors include the stage of cancer, the patient's overall health and medical history, and the potential risks and benefits of the treatment.
It is important to note that CAR T-cell therapy is still relatively new and not yet widely available.
Does this therapy ever fail?
Yes, Car t-cell therapy can fail. It can fail due to several reasons, including:
1. Poor patient selection: If the patient is not an ideal candidate for car t-cell therapy, it may not be successful.
2. Insufficient cell numbers: If not enough t-cells are available to be infused, then the therapy may not be effective.
3. Low-quality cells: If the t-cells are not of good quality, then the therapy may not be successful.
4. Inadequate monitoring: If the patient is not monitored properly during the treatment, the therapy may not work.
5. Side effects: Car t-cell therapy can have serious side effects, including cytokine release syndrome, which can lead to serious complications.
What happens if CAR- T cell therapy fails?
If CAR T-cell therapy does not achieve the desired results, other treatment options may be considered. These may include:
- Different types of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy
- Clinical trials for new treatments that are not yet widely available
- Stem cell transplant or Car T-cell transplant to rebuild the immune system (for certain types of cancer)
- The specific action plan will depend on the individual patient and the circumstances.
- Factors that can affect the success of CAR T-cell therapy include:
- The type and stage of the cancer being treated
- The patient's overall health and medical history
- The specific type of CAR T-cell therapy being used
In what cases does CAR-T therapy treatment for cancer fail?
There are a number of factors that can affect the success of CAR T-cell therapy for cancer, and in some cases, the treatment may not achieve the desired results. Car T therapy treatment for cancer can fail in cases where -
- If cancer cells have mutated and become resistant to the therapy.
- If the patient’s immune system is not strong enough to effectively target the cancer cells.
- If too few T cells can be harvested from the patient and engineered to recognize the cancer cells, the treatment may not be successful.
- If cancer has spread too widely, it may be difficult for the engineered T cells to reach and eliminate all of the cancer cells.
CAR-T is still in the early stages of development and not widely available globally. More research is still needed to fully understand its potential long-term benefits and risks. Also, the cost of treatment is high and remains a barrier for many patients to access the treatment.
Despite these challenges, the success of CAR-T therapy so far, coupled with ongoing research and development, suggests that it has the potential to become a significant player in the cancer treatment landscape and save many lives.
Note: CAR- T cancer treatment is still relatively new and not yet widely available. But it is being studied in clinical trials for the treatment of a variety of cancer types.