Overview
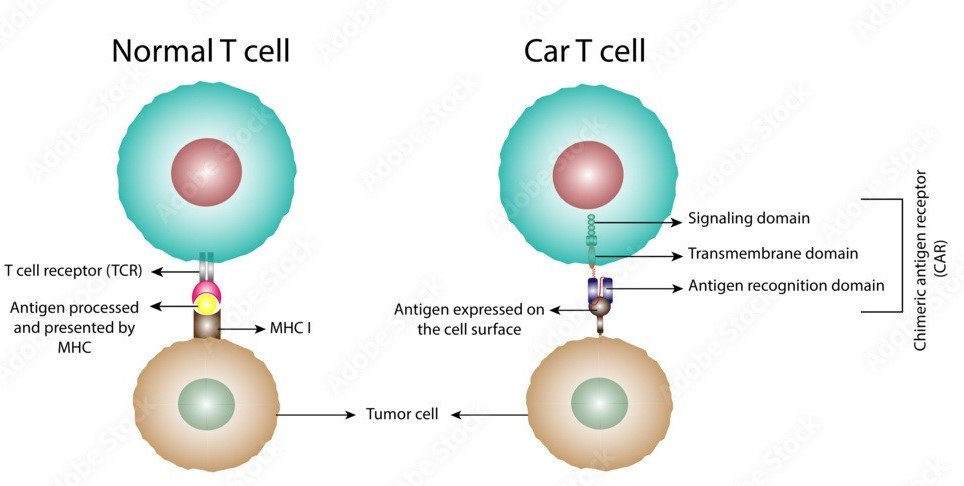
CAR-T cell therapy is a method of modifying immune cells called T cells (a type of white blood cell) in the lab to fight cancer. CAR T-cell therapy includes changing the genes within T cells to enable them to fight cancer. It is occasionally referred to as a form of cell-based gene therapy. CAR-T is primarily used for blood cancers—leukemia and lymphoma. It addresses large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and multiple myeloma.
CAR-T cell therapy is a revolutionary treatment that is now available in India. It is a type of immunotherapy where doctors collect immune cells from a patient, modify them in a lab to fight cancer, and infuse them back into the patient.
Are you also interested in CAR-T cell therapy? Book a consultation with the best oncologists to learn more about your advanced treatment options!
Car-T Cell Therapy in India: Current Status and Availability
We, as Indians, are proud to share a landmark achievement in India's medical history. On April 4, 2024 Our honorable President Smt. Droupadi Murmu introduced the nation’s first indigenously developed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. This groundbreaking therapy, known as actalycabtagene autoleucel (actaly-cel, marketed as NexCAR19), represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment.
Developed through the collaborative efforts of leading scientists from the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, and Tata Memorial Hospital, in partnership with ImmunoACT, this innovative therapy offers new hope for patients.
In October 2023, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization of India approved actually-cel for treating relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas and leukaemia in patients aged 15 and above, making it the first CAR T-cell therapy available in the country.
This achievement highlights the remarkable progress in India's biotechnology sector and sets a new benchmark for future advancements in cancer therapy.
Availability of CAR-T cell therapy at cancer centres in India
1. Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai
- Start Date: June 2021
- Type of CAR-T Cell: Autologous CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Tata Memorial Centre was the first in India to initiate CAR-T cell therapy. They offer CD19-targeted CAR-T cells for treating relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). This pioneering step has made them a leader in advanced cancer treatments in the country.
2. Apollo Hospitals, Chennai
- Start Date: October 2022
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells (CAR-T 19)
- Apollo Hospitals, Chennai, began offering CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy in October 2022, focusing on B-cell malignancies like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). This initial therapy was based on internationally developed technologies.
Evolution to Indigenous Therapy:
- NexCAR19 Launch Date: April 2024
- In a groundbreaking move, Apollo Cancer Centres became India's first private hospital group to complete a CAR-T cell therapy program and introduce NexCAR19, an indigenous CAR-T cell therapy, approved in October 2023. Developed locally through a collaboration with IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Hospital, and ImmunoACT, NexCAR19 is designed to treat B-cell lymphomas and ALL more effectively and affordably, marking a significant advancement in India’s cancer treatment capabilities.
3. Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore
- Start Date: February 2023
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19 and BCMA-targeted CAR-T cells
- CMC Vellore provides CD19-targeted CAR-T cells for B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and BCMA-targeted CAR-T cells for multiple myeloma. Their comprehensive oncology department offers these advanced treatments as part of their commitment to innovative cancer care.
4. HCG Cancer Centre, Bengaluru
- Start Date: January 2023
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- HCG Cancer Centre in Bengaluru has integrated CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for patients with B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). They emphasize a multidisciplinary approach, ensuring patients receive the most effective treatment tailored to their needs.
5. AIIMS, New Delhi
- Start Date: September 2021
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- AIIMS New Delhi offers CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy, focusing on treating relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). As a premier medical institution, AIIMS combines cutting-edge research with patient care, making advanced treatments like CAR-T therapy accessible to a broader population.
6. Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- Start Date: March 2023
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon began providing CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Their state-of-the-art facilities and expert team are dedicated to delivering advanced cancer care options.
7. Max Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi
- Start Date: April 2023
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Max Super Speciality Hospital in New Delhi started offering CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The hospital focuses on personalized patient care and integrates innovative therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
8. Jaslok Hospital and Research Centre, Mumbai
- Start Date: November 2022
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Jaslok Hospital in Mumbai provides CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy, primarily for treating B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The hospital’s experienced oncology team ensures that patients receive the latest cancer treatment technologies.
9. Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre, New Delhi
- Start Date: December 2022
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute in New Delhi offers CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for patients with B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). They are known for their focus on advanced cancer care and research, providing access to state-of-the-art treatments.
10. Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi
- Start Date: January 2023
- Type of CAR-T Cell: CD19-targeted CAR-T cells
- Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences in Kochi started providing CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy for B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Their comprehensive cancer care program includes this innovative treatment, supported by a multidisciplinary team of experts.
Each of these centers has embraced CAR-T cell therapy, marking a significant advancement in cancer treatment in India. They offer hope to patients with certain types of cancers resistant to conventional treatments, providing access to one of the most advanced therapies available today.
Types of cancers treated with car-T cell therapy in India
As of October 2023, Car-T cell therapy in India is currently approved for only one type of cancer:
- Relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas: NexCAR19, the only commercially available CAR-T therapy in India, is approved for treating patients with some types of B-cell lymphomas that haven't responded to standard therapies. This includes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
However, several clinical trials are ongoing for CAR-T cell therapy in India, targeting a wider range of cancers, including:
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Multiple myeloma
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Glioblastoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
The first thing one thinks when considering treatment is “How much will it cost?”
If so, we have the answer to your question.
We have discussed the costs of CAR-T cell therapy in India and everything else you need to know below:
The Cost of CAR-T Cell Therapy in India
- The Made in India Initiative NexCAR19 costs approximately Rs 40 lakh (50,000 USD). While in the United States, CAR T-cell therapies can cost up to $400,000 per dose. This includes:
- Manufacturing and processing: Engineering and expanding T cells involves complex and expensive procedures.
- Hospitalization and supportive care: Monitoring and potential side effect management during inpatient stays add to the overall cost.
Factors influencing the costs of CAR-T cell therapy
- Complex manufacturing: Extracting, engineering, and expanding T cells is labor-intensive and requires sophisticated technology.
- Specialized infrastructure: Dedicated facilities, advanced equipment, and trained personnel are essential for safe and effective treatment.
- Hospitalization and supportive care: Inpatient stays and potential side effect management add to the financial burden.
- Limited market availability: Few manufacturers and ongoing research & development contribute to higher prices.
- Lack of insurance coverage: Many plans don't yet cover CAR-T cell therapy, leaving patients responsible for hefty costs.
If you are considering CAR-T cell therapy you should know how much will it cost.
We have presented the costs of CAR-T cell therapy in various countries.
Check them out!
The table below compares the CAR-T cell therapy costs in different countries:
| Country | Cost |
| USA | $400,000 - $700,000 |
| UK | $450,000 |
| Singapore | $450,000 |
| Korea | $450,000 |
| Japan | $500,000 - $750,000 |
| China | $300,000 - $600,000 |
| Malaysia | $500,000 - $700,000 |
Please Note: The above-mentioned costs are generalized. Actual prices may differ based on several factors.
CAR-T cell therapy is very promising, however, everyone can't undergo this treatment. We have presented the eligibility criteria below.
So please pay attention!
Eligibility criteria for CAR-T cell therapy in India
In India, CAR-T cell therapy eligibility criteria depend on the specific therapy and cancer type, but generally encompass these factors:
1. Type and stage of cancer: Currently, NexCAR19 is approved only for specific relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas like DLBCL, FL, and MCL. Clinical trials are ongoing for other cancers.
2. Overall health: Patients must be physically strong enough to tolerate the treatment and potential side effects. Underlying medical conditions may affect eligibility.
3. Prior treatments: Successful response to standard treatments and absence of certain prior therapies are often required.
4. Age: Although age itself isn't a strict criterion, younger patients generally have better health and tolerance for the treatment.
5. Availability: Limited access to specialized centers and trained personnel in India affects overall availability.
6. Cost: High treatment costs and limited insurance coverage remain a significant barrier for most patients.
How is Car-T cell Therapy administered?
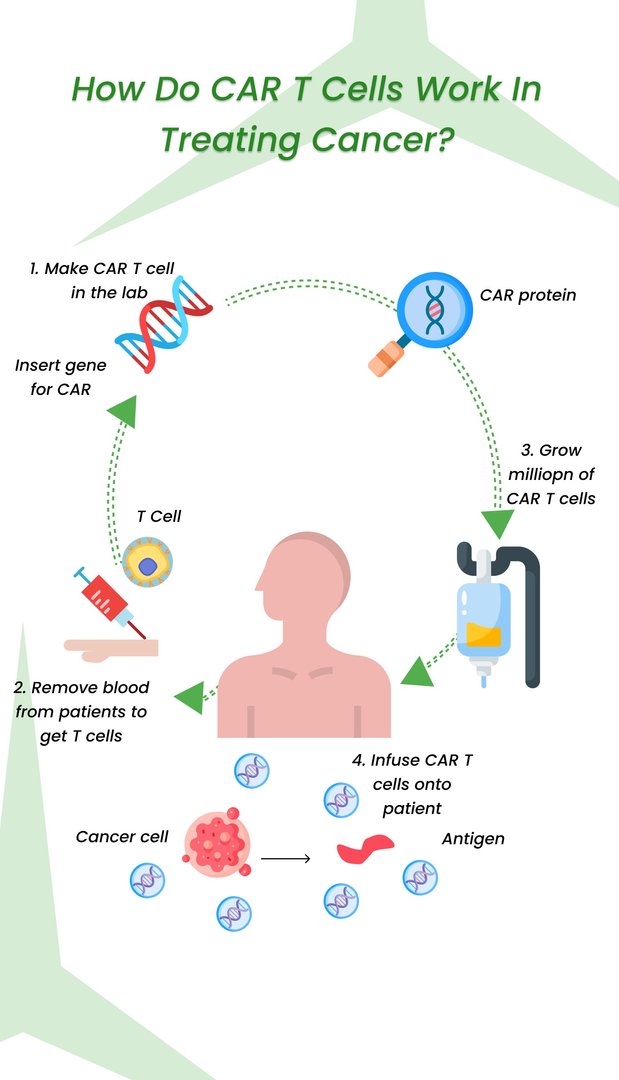
The procedure for Car-T cell therapy in India follows a similar process as elsewhere but with some adjustments due to the limited availability and ongoing development of this treatment:
1. Pre-treatment:
Patient eligibility: Comprehensive patient evaluation to determine if they are a suitable candidate for CAR-T therapy, considering factors like type and stage of cancer, overall health, and potential for side effects.
Lymphodepletion (optional): In some cases, patients may receive chemotherapy or other agents to reduce their existing T cell population before CAR-T cell infusion. This creates space for the infused CAR-T cells to expand and function effectively.
Apheresis: Blood extraction (similar to a blood donation) to collect T cells from the patient.
2. Manufacturing:
T cell isolation: Separating the extracted T cells from other blood components.
CAR T-cell engineering: The isolated T cells are genetically modified in a laboratory to express the Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) that targets specific cancer cells. This is usually done by infecting the T cells with a viral vector carrying the CAR gene.
Expansion and activation: The engineered CAR-T cells are cultured in the lab to increase their number and enhance their anti-tumor activity.
3. Post-treatment:
CAR-T cell infusion: Once sufficient CAR-T cells are available, they are infused back into the patient's bloodstream through an intravenous catheter.
Monitoring and management: Close monitoring for potential side effects like cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity. Supportive care and symptom management as needed.
Follow-up and monitoring: Regular medical evaluations to track the effectiveness of the treatment and manage any long-term side effects.
Just like any other treatment, CAR-T cell therapy has benefits as well as challenges. We have presented them below.
So, please read them carefully!
Advantages and Limitations of CAR-T Cell Therapy
Highly Effective Targeting:
- Remarkable success against specific cancers, especially relapsed B-cell lymphomas.
- Higher remission rates compared to conventional therapies.
Personalized Approach:
- Engineered T cells specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Offers a more targeted and potentially safer treatment approach.
Long-term Remission:
- CAR-T cells can persist in the body, providing prolonged remissions.
- Reduces the need for repeated treatments.
Hope for Advancements:
- Ongoing research in India aims for indigenous CAR-T therapies.
- Promises broader accessibility and affordability in the future.
High Cost Barrier:
- Current high cost restricts access for many patients.
- Limits availability across various income levels.
Limited Availability:
- Only one approved commercially available CAR-T therapy (NexCAR19).
- Access is mainly restricted to specialized centers, creating geographical limitations.
Potential Side Effects:
- Can cause severe side effects like cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity.
- Requires close monitoring and supportive care.
Insurance Coverage Gap:
- Most insurance plans in India don't cover CAR-T therapy.
- Leaves patients to bear the financial burden entirely.
Early Development Stage:
- Promising Indigenous CAR-T therapies are still in development and clinical trials.
- Requires further research and evaluation for broader application.
Long-Term Effects of CAR-T Cell Therapy
Car-T cell therapy, while revolutionary, carries potential long-term effects still under investigation. Here's a summary:
- Positive Effects:
Durable remission: Engineered T cells can persist in the body, potentially offering long-term remissions and reducing the need for repeated treatments.
Improved quality of life: Successful treatment can lead to improved physical and mental well-being for cancer survivors.
Advancements in technology: Ongoing research continuously improves efficacy and safety profiles, potentially offering improved long-term outcomes in the future.
- Negative Effects:
Relapse: While promising, relapse is still possible, depending on cancer type and individual factors.
Cytopenias: Long-term depletion of certain blood cell types (T cells, B cells) can increase susceptibility to infections, requiring monitoring and potential supportive treatments.
Autoimmune reactions: CAR-T cells might attack healthy tissues, leading to autoimmune disorders, though the risk is generally low.
Effects on the immune system: The overall impact of manipulating the immune system in the long term is still being researched.
Psychological effects: The high cost, complexity, and potential side effects of the treatment can lead to anxiety and stress for patients, requiring psychosocial support.
Get comprehensive information about CAR-T cell therapy in India. Book an appointment with top Oncologists for detailed insights and make informed decisions for your health.
Future prospects of the use of CAR-T cell therapy in India
While current access to Car-T cell therapy in India faces hurdles, the future holds promising prospects for expanded usage and accessibility:
Increased Availability:
- More indigenous therapies: Local companies are developing affordable CAR-T options, potentially bringing down costs and expanding access.
- Growing infrastructure and personnel: More specialized centers and trained professionals are expected to emerge, improving geographical reach.
- Clinical trial advancements: Ongoing trials for various cancers could lead to approvals for a wider range of applications.
Improved Affordability:
- Government support: Initiatives like subsidies and financial assistance programs could ease the financial burden for patients.
- Insurance coverage expansion: More insurance companies are starting to cover Car-T cell therapy, offering hope for increased access.
- Innovative payment models: Payment plans and crowdfunding efforts could be explored to mitigate the upfront cost barrier.
Technological Advancements:
- Streamlined manufacturing: New techniques could decrease production costs and processing time, making the therapy more efficient.
- Safer and more effective CAR-T cells: Research on enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects continues, improving patient outcomes.
- Off-the-shelf CAR-T cells: Pre-manufactured, universal CAR-T cells could reduce dependence on individual patient processing, making treatment faster and more readily available.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1465324921008239
https://actrec.gov.in/node/2416
https://www.kimshospitals.com/