Cancer is a scary and life-threatening disease. The treatment options are limited for cancer, but if it is detected early, the chances of successful treatment can increase. Pancreatic cancer is not found until it has reached the advanced stages. This is because of the organ's location, and the doctors don't feel your pancreas while performing a routine check-up. So if you don't see any symptoms, cancer can go undetected for a while.
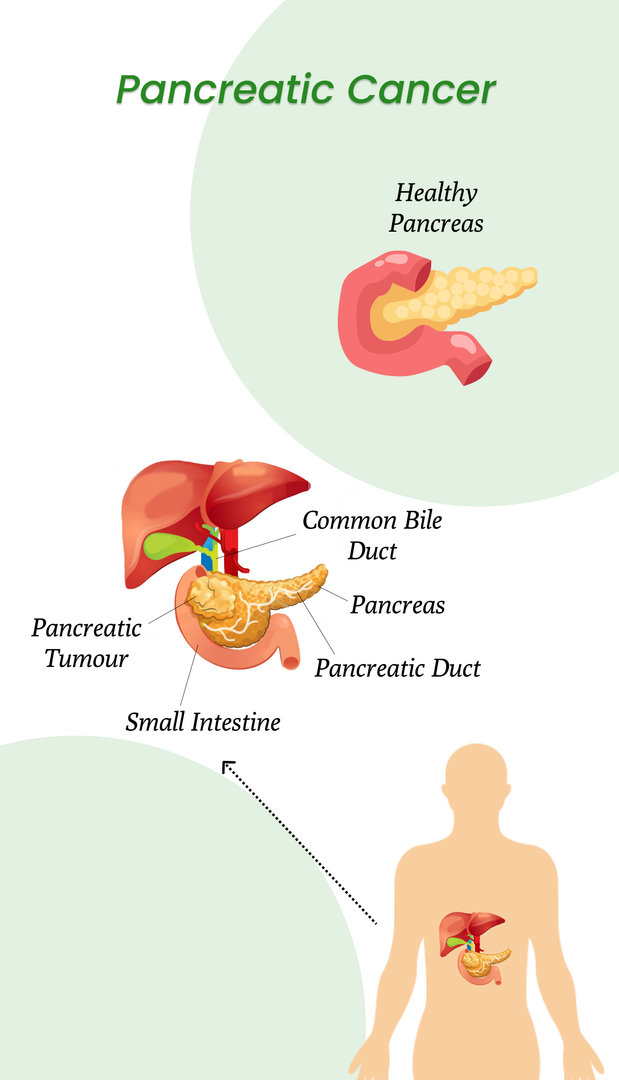
This question will definitely arise in your mind when we already have pancreatic cancer treatment. Well, let's read ahead to know it in a better way.
In the case of pancreatic cancer, no existing screening tests can detect pancreatic cancer in the earlier stages. The research is going on to develop a tool that can detect cancer earlier.
The main reason there is a need for a new treatment for pancreatic cancer is that this cancer is tough to treat. Research teams around the globe are trying to find new ways to treat this disease.
Until recently, pancreatic cancer was treated using surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These treatments were effective in treating systemic pancreatic cancer; it is cancer that has spread to the other parts of your body.
Now, researchers are focusing on developing treatments that will be more targeted in how they will attack cancer cells. These developing medicines have the potential to fundamentally alter how doctors treat pancreatic cancer today and in the future, but more research is required.
Latest Treatment for Pancreatic Cancer 2022: New Hope
In a clinical trial project for groundbreaking pancreatic cancer treatment, medical experts from the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the Australian biotechnology company Amplia Therapeutics are making a significant milestone.
They contend that the new targeted therapy can increase the susceptibility of cancer tumors to chemotherapy and raise patient survival rates.
The clinical trials can destroy the pancreatic tumor cancer cells for the novel medication AMP945.
The focus of AMP945 will be on the survival rates of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, one of the worst diseases in the world and an aggressive form of pancreatic cancer.
The 5-year survival rate is less than 10%, and if cancer has spread to other body areas, it will fall below 3%.
What is the Strategy for Pancreatic Cancer New Treatment?
A protein produced by pancreatic cancer cells is the target of AMP945. The protein is known as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), which regulates fibrotic tissue growth.
Initial studies have produced encouraging results for the novel strategy of treating the tumor's surrounding tissue while also administering conventional chemotherapy.
“We wanted to try to improve chemotherapy by applying a novel strategy - targeting the environment around the tumor to make cancer more receptive to treatment,” says Dr. David Herrmann, co-leader of the study from Garvan's Invasion and Metastasis Lab.
At Garvan, preclinical studies showed that AMP945 could successfully inhibit FAK and reduce the stiffness and density of the connective tissue or stroma around cancer cells.
You must be interested to know how the study has been done. Let's read along..
How is the experiment done on the new drug for pancreatic cancer?
Experimental: AMP945
Part A: Cohorts of patients receiving AMP945 at increasing doses.
Part B: Recommended phase 2 dosage for AMP945
Treatment
Drug: AMP945 in escalating dosages
Part A is a phase 1b dose-escalation design that will enroll at least three patients in each of the four dose-level cohorts to assess the RP2D of AMP945, which will be evaluated in Part B. The dose-escalation decisions will be based on a standard 3+3 dose-escalation phase 1 oncology trial design.
Drug: AMP945 RP2D
The effectiveness of the AMP945 priming regimen at the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D), as calculated in Part A, will be assessed in AMP945 RP2D Part B.
Outcome Measures:
Primary Outcome
Measure |
Time Frame |
Number of participants with TEAEs (Treatment Emergent Adverse Events) from baseline to End of the study
| An average of six months should pass between the first study drug dose and its conclusion. |
Part A: Determination of RP2D
|
Following Cycle 1 (28 days) for each cohort in Part A |
Part B: efficacy of AMP945
|
Imaging every 56 days per participant, with an expected average duration of 6 months
|
Secondary Outcome
Measure |
Time Frame |
Part A: efficacy of AMP945 |
With an anticipated average duration of 6 months, imaging is performed every 56 days per participant. |
AMP945 levels in plasma
|
Days -8, -7, 1, 3, 4, 8 and 10 |
AMP945 levels in plasma
|
Days -8, -7, 1, 3, 4, 8 and 10 |
AMP945 levels in plasma
|
Days -8, -7, 1, 3, 4, 8 and 10 |
Is any further trial required for this new drug for pancreatic cancer?
Yes. AMP945 trial is now recruiting people with advanced pancreatic cancer for the next trial. Notably those with inoperable pancreatic cancer or whose cancer has progressed to other parts of the body and has not previously had chemotherapy.
In an animal model using human pancreatic cancer cells, AMP945 increases the efficacy of the current standard of therapy.
Pre-treatment with AMP945 enhanced survival by 33% when used with the chemotherapy regimen of gemcitabine and Abraxane®.
Confirmation in a second animal model further supports the logic and layout of AMP945's Phase 2 human trial in people with first-line pancreatic cancer. In a recent news Amplia CEO and Managing Director, Dr. John Lambert said,
“Reaching a Phase 2 clinical trial milestone for AMP945 represents an important achievement for Australia’s medical research and biotechnology sector, signaling the translation of a novel therapy – discovered and developed by Australian scientists – into a tangible and potentially life-saving treatment for people with pancreatic cancer.”
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most challenging cancers to treat. It does not get detected until a progressed stage, so it is essential to have a new pancreatic cancer treatment as it is a life-threatening disease. The research for the new drug for pancreatic cancer can be beneficial in saving people's lives.
References: