Before we begin you need to understand what is bone marrow:
Bone marrow is the semi-solid sponge like tissues present in the center of most bones, primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, breastbone, and bones of the pelvis. It includes stem cells that ultimately forms blood cells like white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets.
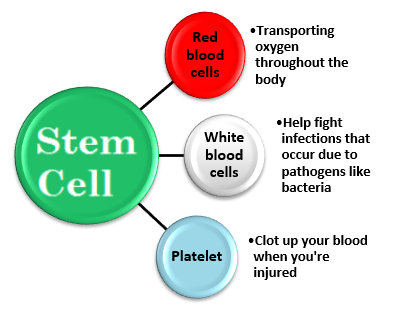
Bone marrow is where your hematopoietic stem cell are ultimately produced which help to make red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
The blood related diseases and cancers cause the cells to behave anti-socially.
This leads to abnormal behaviors such as un-controlled cell growth or breaking down of blood cells.
Treatment options used to treat these anomalies such as chemotherapy and radiation are given to you to kill all the damaged cells.
But these treatments attack both the good and bad cells.
Since stem cells contain immunity cells that help the body fight from infections and diseases, including cancer, it is important that they are replaced by a healthy bone marrow.
Usually, Bone marrow transplant is not the first line of treatment.
It is done when the bone marrow is unable to or not healthy enough to produce healthy cells and perform its functions due to chronic infections, disease or cancer treatments.
Hence the transplant is one of the last resorts for treating blood cancers and disorders prescribed by oncologist in India.
Cancers & Disorders that require Bone Marrow Transplants:
- Cancers that affect the marrow, such as Leukemia (unchecked growth of damaged blood cells), lymphoma (effects a type of white blood cells known as lymphocytes), and multiple myeloma (plasma cells become cancerous and grow out of control)
- Damaged bone marrow due to chemotherapy or radiation.
- Congenital neutropenia, which is an inherited disorder that causes recurring infections.
- Sickle cell anemia, which is an inherited blood disorder that causes red blood cells to misshapen and break down.
- Aplastic anemia, a rare condition in which the marrow stops making new blood cells.
- Thalassemia
Generally there are two ways that bone marrow transplant is done i.e. autologous and allogeneic. And both of these are used to treat different type of cancers. This can be classified as follows:
Autologous stem cell transplant:
Allogeneic Stem cell transplant:
- Acute Myeloid leukaemia
- Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Myeloproliferative disorders
- Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
- Hodgkins Lymphoma
- Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia
- Multiple Myeloma
- Aplastic anemia
- Thalassemia
- Fanconi’s anemia
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia