What is ACL reconstruction with hamstrings?
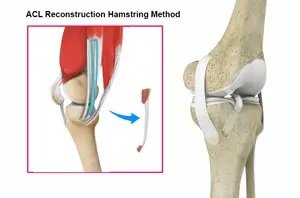
The ACL reconstruction with hamstrings is a surgical procedure. It involves replacing the injured ACL with a hamstring tendon. The ACL is crucial for stabilizing the knee joint. Thus is needed to prevent excessive forward and rotational movements of the knee. When the ACL is torn, it can lead to knee instability. So, the reconstruction surgery aims to restore stability by using a tissue graft to reconstruct the torn ligament.
There can be various causes of ACL injury. These are some of the few most probable ones:
- ACL injuries frequently happen during sports. Mostly during activities that involve twisting or overextending the knee.
- Sudden directional changes or slowing down while running.
- Direct blows to the side of the knee. For example, during a football tackle.
Continue reading to discover the ground-breaking technique of ACL reconstruction using a hamstring graft. A game-changing surgery that promises strength, stability, and a faster recovery!
Is hamstring graft stronger than normal ACL?
ACL reconstruction with hamstring involves obtaining two hamstring tendons. They are obtained through a small incision below the knee. These tendons are then doubled over to create a quadruple graft. This makes it very strong, up to two or three times the strength of the native ACL.
The hamstring graft has shown several benefits. They include:
- Better knee extension
- A lower incidence of post-surgical arthritis
- Improved extension strength.
A study on high-performance athletes revealed that 98 out of 113 were able to return to their pre-injury activity level after the surgery.
Patients who undergo hamstring grafts experience a reliably stable knee with proper function. This enables them to return to sports and an active lifestyle confidently.
Wondering how surgeons perform hamstring graft harvesting? Uncover the surgical secrets behind this powerful technique.
How is the hamstring graft harvested?
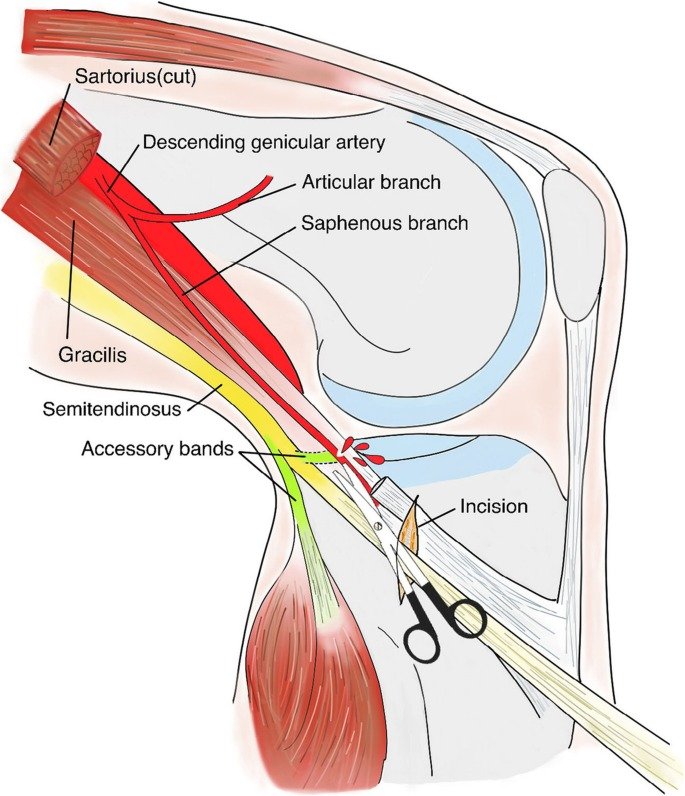
The semitendinosus (ST) or gracilis (GC) tendons are the two options for harvesting. These tendons can be taken from either the same knee or the opposite knee. The procedure requires making a vertical anteromedial incision. This incision is made around the level of the tibial tubercle to access the tendons.. This incision allows access to the sartorius fascia and pes anserine bursa. It covers the hamstring tendons.
by creating an incision in the sartorial fascia, the surgeon exposes the hamstring tendons. Each tendon is individually identified and then passed through an open tendon stripper. While the stripper is advanced in the proximal direction. This technique ensures the safe and effective harvest of the hamstring tendons.
Are you ready to experience a stronger, more durable ACL reconstruction? Discover the remarkable advantages of the hamstring graft.
What are the advantages of using a hamstring graft?
Getting ACL reconstruction with hamstring graft offers several advantages:
- Strength and Durability: The quadruple hamstring graft consists of four tendon strands. This provides exceptional strength and durability. It can withstand the demands of sports and high-impact activities. This ultimately reduces the risk of re-injury.
- Reduced Donor Site Morbidity: The harvest of hamstring tendons typically leads to less postoperative pain and discomfort. This results in quicker recovery and rehabilitation.
- Better Knee Extension: Patients who receive hamstring grafts often experience better knee extensions. This improves overall knee function and range of motion.
- Improved Cosmesis: The small incision used to harvest the hamstring tendons results in minimal scarring.
- High Return to Activity Rate: Many individuals who undergo ACL reconstruction with hamstring grafts recover faster. They are able to return to pre-injury activity levels much earlier without any issues.
Eager to get back on your feet after ACL surgery? Dive into the comprehensive recovery process.
What is the recovery process like after ACL reconstruction with a hamstring graft?
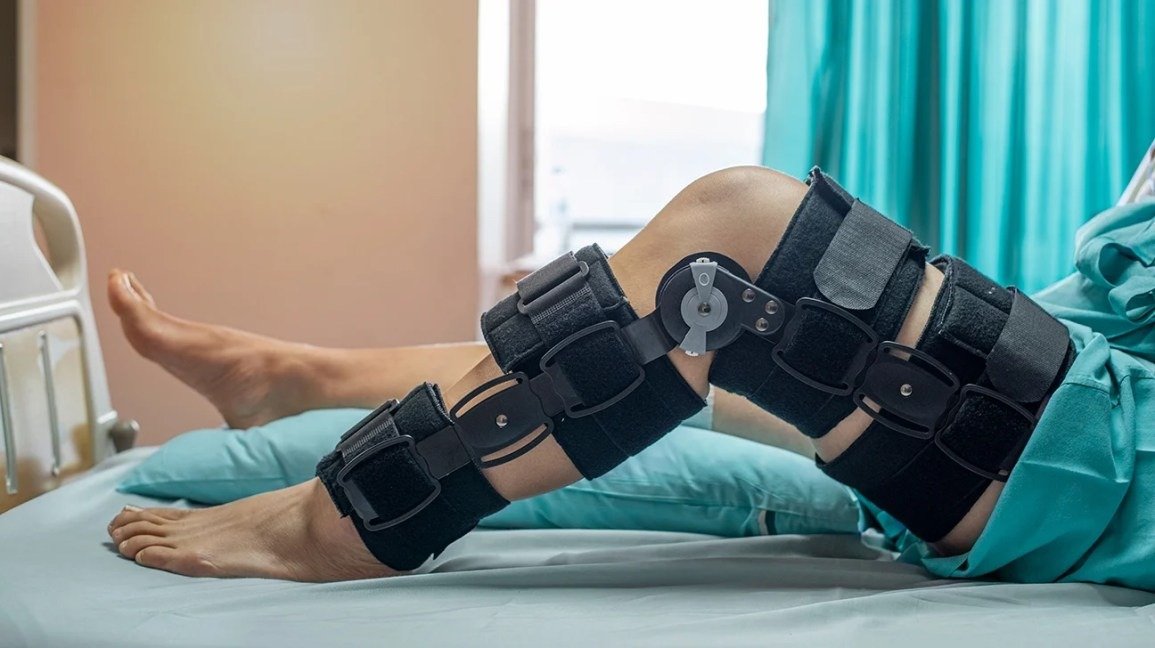

After ACL reconstruction with a hamstring graft, the recovery process involves several stages:
- Immediate Post-Surgery: Close monitoring in the recovery room. pain management and wound care.
- Initial Rest and Rehabilitation: Crutches, knee braces, and physical therapy to improve mobility and reduce swelling.
- Weeks 2 to 6: Focus on knee motion and muscle strengthening.
- Months 3 to 6: Transition to weight-bearing exercises and functional activities.
- Months 6 to 12: Continued strengthening and sports-specific training.
- After 1 year: Return to sports allowed after evaluation.
The whole process of rehabilitation and recovery is monitored by a physiotherapist. The process involves activities like swimming, bike riding, muscle strengthening and proprioceptive exercises.
Worried about re-injury after surgery? Learn invaluable tips and techniques to protect your knees. Achieve a successful, long-lasting recovery.
Can you prevent re-injury after ACL reconstruction with a hamstring graft?
Before ACL reconstruction surgery, discuss with your doctor the type of graft tissue that will be used. Ensure the surgeon uses up-to-date techniques for proper graft placement to avoid re-rupture.
- Returning to sports too soon after surgery increases the risk of re-injury. So, give the graft enough time to heal fully (8 to 12 months).
- Focus on strengthening quadriceps, hamstrings, and thighs to protect the knees.
- Physical therapy is crucial for restoring range of motion, strength, and balance.
- Improve balance through exercises or Yoga to aid recovery. This ensures movements become innate again.
What is the success rate of ACL reconstruction with hamstrings?
The success rate of ACL reconstruction with hamstring grafts is generally high. The success rate ranges from 82% to 95%. Most patients experience improved knee stability and function after surgery.
However, the success of the procedure can vary depending on various factors:
- Surgeon's skill
- Patient's commitment to rehabilitation
- Adherence to post-surgery guidelines